Sometimes, we find ourselves immersed in vivid night visions that leave us feeling perplexed and curious about their underlying meanings. Our slumbering minds often conjure up scenarios that reflect our subconscious anxieties or desires. One of the recurring motifs is the presence of discomfort or abnormalities within our bodies, particularly in sensitive areas such as our oral cavity. These nocturnal episodes filled with unsettling imagery and sensations prompt us to delve deeper into the realm of tongue anomalies, seeking to unravel the intricate web of potential triggers, symptoms, and possible treatments.
While we may not be able to recall the exact content of our sleep-inspired voyages to the uncharted territory of tongue afflictions, the lingering sense of unease and curiosity keeps us pondering throughout the day. Tongue ailments, like enigmatic puzzles, can reveal themselves in a multitude of forms, each carrying a unique set of signs and consequences. It is in this state of inquisitiveness that we embark on a journey to enlighten ourselves about what lies beneath the surface of these dream-infused enigmas.
As explorers of the dark recesses of our subconscious, we are intrigued by the elusive culprits behind tongue ailments. These unwelcome intruders can enter our lives through various gateways, ranging from bacterial or viral invasions to underlying medical conditions or allergic reactions. Discovering their point of entry is paramount in deciphering our nocturnal ordeals. By delving into the intricate nuances between these potential causes, we can unravel the mysteries surrounding tongue afflictions, shining a light on the path towards relief and tranquility.
Unveiling the symptoms that accompany tongue irregularities serves as a compass, guiding us through the unfamiliar territory of our dreams and realities. It is through these indicators that we can differentiate between normal variations in tongue appearance and genuine concerns that warrant medical attention. Whether our taste buds are beset by discomfort, our tongues bear strange coatings, or we experience heightened sensitivity, these manifestations act as beacons illuminating the potential presence of an underlying infection. Recognizing and understanding these signals awakens our curiosity and leads us to embark on a journey towards discovering effective remedies that restore harmony to our tongues and bring solace to our sleeping souls.
Understanding the Origins of Tongue Infections
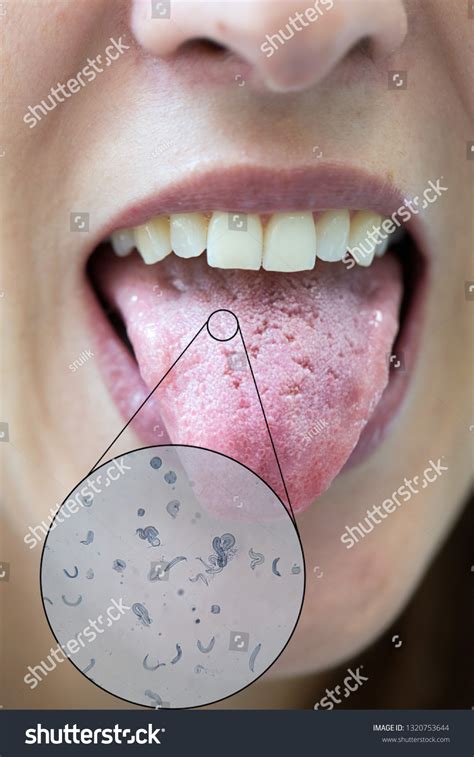
In the realm of understanding tongue-related ailments, it is crucial to delve into the causes that give rise to infections affecting this vital organ. By exploring the underlying factors that contribute to the development of such conditions, a clearer picture can be gained and appropriate treatment measures can be carried out effectively.
Bacterial invasion: One of the primary causes of tongue infections is the invasion of harmful bacteria into the oral cavity. Unhealthy oral hygiene practices, such as inadequate brushing and flossing, create an environment that is conducive to bacterial growth and colonization on the tongue's surface. This bacterial overgrowth can lead to various forms of infections, causing discomfort and hindering proper oral function.
Fungal overgrowth: Another significant cause of tongue infections is the overgrowth of fungi, particularly Candida species. When the delicate balance of microorganisms in the mouth is disrupted, Candida can multiply rapidly, leading to conditions like oral thrush or candidiasis. Factors such as a weakened immune system, certain medications, or hormonal imbalances may contribute to the occurrence of fungal infections on the tongue.
Injury or trauma: Tongue infections can also be a result of injury or trauma to the tongue. Accidental biting, sharp-edged foods, or dental procedures that involve the tongue can lead to the introduction of foreign substances or bacteria into the tongue, causing inflammation and subsequent infection.
Usage of irritants: The prolonged usage of substances that irritate the tongue can also pave the way for infections. Habits such as tobacco use, excessive alcohol consumption, or regularly consuming spicy and acidic foods can irritate the delicate tissues of the tongue, making them more susceptible to infection.
Underlying medical conditions: In some cases, tongue infections can be a manifestation of underlying medical conditions. Certain systemic conditions, like diabetes or autoimmune disorders, can weaken the immune system, making the tongue more prone to infections. Additionally, nutritional deficiencies, hormonal imbalances, and chronic diseases can compromise the tongue's overall health, increasing the risk of infection.
Understanding the diverse causes behind tongue infections is crucial in both the prevention and treatment of such conditions. By addressing these underlying factors, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain optimal oral health and minimize the risk of tongue infections.
Bacterial Infections: Common Culprits
When it comes to the potential causes of tongue infections, bacteria can often be held accountable. These microscopic organisms are well-known troublemakers when it comes to oral health, and they can find their way into the tongue and wreak havoc. In this section, we will explore some of the most common types of bacterial infections that can affect the tongue, highlighting their characteristics and discussing potential treatment options.
1. Streptococcus pyogenes: Also known as Group A Streptococcus, this bacterium is a frequent culprit in causing tongue infections. It is notorious for causing strep throat, but it can also lead to inflammation and infection in the tongue. This condition, known as glossitis, can cause pain, redness, and discomfort. Treatment usually involves antibiotics to combat the bacterial infection.
2. Staphylococcus aureus: This type of bacteria, commonly referred to as Staph, can also be responsible for tongue infections. Staphylococcus aureus can be found in the nose and throat of many healthy individuals, but under certain conditions, it can cause infections in various parts of the body, including the tongue. Treatment often involves antibiotics specific to Staphylococcus aureus strains.
3. Fusobacterium nucleatum: This bacterium is a common resident in the oral cavity and is known to contribute to dental plaque formation. However, when it proliferates excessively, it can lead to tongue infections. Fusobacterium nucleatum infections can manifest as localized redness, swelling, and discomfort on the tongue's surface. Treatment usually involves good oral hygiene practices and, in severe cases, antibiotics may be prescribed.
4. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Although more commonly associated with hospital-acquired infections, Pseudomonas aeruginosa can also find its way to the tongue and cause infections. This bacterium is known for its resilience and ability to thrive in moist environments. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections on the tongue can result in ulcerations, foul odor, and an unpleasant taste in the mouth. Treatment typically involves targeted antibiotics and addressing the underlying cause of infection.
Overall, understanding the common culprits behind bacterial tongue infections can help individuals seek appropriate treatment and take preventive measures to maintain optimal oral health. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan to effectively combat these infections.
Viral Infections: Essential Information
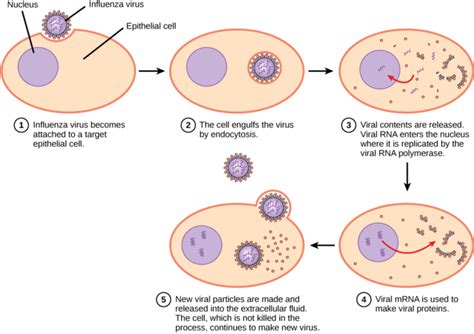
When it comes to viral infections, it is crucial to understand their nature, causes, symptoms, and available treatments. Viruses, unlike bacteria, are microscopic organisms that rely on host cells to replicate and survive. These infectious agents have the ability to invade various parts of the body, causing a range of illnesses.
Causes: Viruses can be transmitted through various means, including direct contact with infected individuals, inhalation of contaminated droplets, or exposure to contaminated surfaces. Different types of viruses have different modes of transmission, such as respiratory droplets for influenza or skin-to-skin contact for herpes.
Symptoms: Viral infections exhibit a wide array of symptoms, depending on the specific virus and affected area of the body. Common symptoms may include fever, fatigue, body aches, respiratory issues, gastrointestinal disturbances, and skin rashes. Some viral infections, like the common cold, may cause mild symptoms, while others, such as viral meningitis, can lead to more severe complications.
Treatments: Unfortunately, there is no specific cure for viral infections. Most viral infections resolve on their own with time as the immune system fights off the invading virus. However, certain antiviral medications can help alleviate symptoms, decrease the duration of illness, and prevent viral replication. In some cases, preventive vaccines are available to protect against specific viral infections, like the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine.
In conclusion, understanding viral infections is essential for identifying the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and undertaking appropriate treatments. By staying informed and practicing proper hygiene, individuals can take steps to prevent the spread of viral infections and protect their overall health.
Fungal Infections: Symptoms and Treatment
Exploring the realm of fungal infections, this section delves into the various indicators and recommended approaches for managing these conditions. Fungal infections, caused by microscopic fungi, present a distinct set of symptoms that require prompt attention. Recognizing the signs can aid in timely treatment and prevention of complications.
Symptoms:
Fungal infections may manifest differently depending on the affected area. Common indicators include redness, itching, and a burning sensation. In some cases, the skin may appear scaly or prone to peeling. Other manifestations can involve the development of painful blisters or the presence of unusual discharge. These symptoms may vary in intensity and duration, depending on individual factors and the specific fungal strain.
Treatment:
Successfully managing fungal infections often involves a multipronged approach. Topical antifungal medications, such as creams or powders, are commonly prescribed to alleviate symptoms and hinder fungal growth. In more severe cases or if the infection has spread extensively, oral antifungal medications may be necessary to combat the infection internally. It is essential to adhere to the prescribed treatment regimen diligently, even if symptoms alleviate, to ensure complete eradication of the fungal infection.
In addition to medication, certain lifestyle modifications can aid in the recovery process and help prevent recurrence. Maintaining good hygiene practices, such as keeping the affected area clean and dry, can inhibit fungal growth. Avoiding sharing personal items like towels or clothing with others can also minimize the risk of infection spread. Utilizing breathable fabrics and wearing appropriate footwear can promote better air circulation and reduce moisture, creating an unfavorable environment for fungal growth.
Please note: While mild fungal infections can often be managed effectively at home with over-the-counter treatments, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and suitable treatment plans, especially when symptoms persist or worsen.
Symptoms of Oral Inflammation
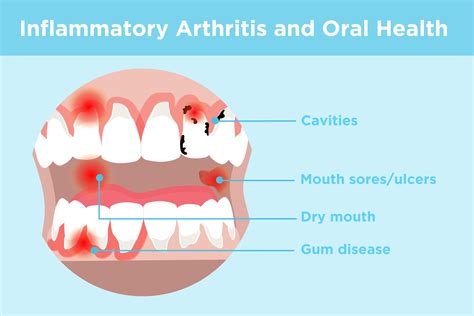
When the tongue is affected by an inflammatory condition, several noticeable indications may arise. These signals can be seen, felt, or experienced by the affected individual, indicating the presence of an oral infection or inflammation.
- Redness: The tongue may appear redder than usual, which is a common sign of inflammation.
- Swelling: If the tongue appears larger than normal, it might be a result of inflammation.
- Pain or discomfort: Individuals may experience aching or discomfort in the tongue, making it difficult to eat or speak.
- Changes in texture: Texture alterations such as bumps, sores, or ulcers on the tongue's surface may indicate an infection.
- Bleeding: If the tongue bleeds without any apparent cause, it could be due to an underlying infection or inflammation.
- Difficulty in swallowing: In certain cases, an infected tongue can make swallowing difficult for individuals.
- Unpleasant breath: People with tongue infections may experience persistent bad breath, which can be embarrassing.
It is important to note that the symptoms mentioned above may vary in intensity depending on the individual and the underlying cause of the tongue infection. These signs serve as key indicators for individuals to seek necessary medical attention for diagnosis and treatment.
Pain and Inflammation: Understanding the Discomfort
When considering tongue issues, it is essential to examine the pain and inflammation that often accompany them. The discomfort experienced by individuals, caused by various factors, can manifest in several ways and have a significant impact on daily life. By understanding the nature of these sensations, one can better comprehend the underlying causes and find the appropriate treatments to alleviate the discomfort.
One common symptom associated with tongue issues is pain, which can range from mild to severe. The discomfort may be sharp, throbbing, or a constant ache, making it difficult to eat, drink, or speak comfortably. Inflammation, on the other hand, refers to the tongue's swelling and redness, which can further intensify the pain and disrupt normal functioning.
The causes of pain and inflammation in the tongue are diverse. It can be a result of an infection, such as a viral or bacterial infection, or an allergic reaction to certain foods or medications. Tongue injuries, such as biting or scalding the tongue, can also lead to discomfort and inflammation. In some cases, underlying medical conditions such as oral thrush, glossitis, or oral cancer may be responsible for the pain and inflammation.
Addressing the discomfort caused by pain and inflammation requires a comprehensive approach. Depending on the cause, different treatments may be recommended. For infections, antiviral or antibacterial medications may be prescribed, while allergies may require avoidance of triggering substances or the use of antihistamines. Proper oral hygiene, including regular brushing and tongue cleaning, can help prevent and alleviate symptoms. Additionally, certain home remedies, such as gargling with warm saltwater or applying ice packs, can provide temporary relief.
- Identifying and addressing potential underlying causes of pain and inflammation
- Seeking medical advice and appropriate treatment options
- Practicing good oral hygiene to prevent discomfort
- Exploring home remedies for temporary relief
By understanding the discomfort associated with pain and inflammation in the tongue, individuals can take proactive measures to alleviate their symptoms, improve their oral health, and enhance their overall well-being.
Changes in Tongue Color: Indicators of Potential Issues
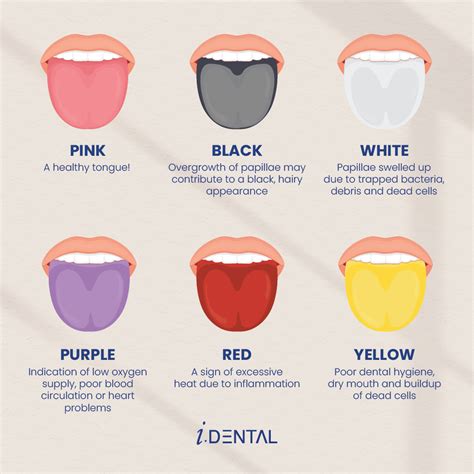
Examining the color of your tongue can provide valuable insights into your overall health. The shade of your tongue can vary from person to person and may change due to numerous factors. Here, we will explore the different colors your tongue may take on and what they potentially indicate.
- White coating: A white coating on the tongue could be a sign of a fungal infection or a build-up of bacteria. It may also indicate dehydration or dry mouth.
- Yellow discoloration: A yellow-colored tongue can suggest an accumulation of dead cells or bacteria. It may also be a sign of jaundice or a liver issue.
- Redness: Redness on the tongue may stem from inflammation, infections, or vitamin deficiencies. It may also be a sign of a more serious condition, such as scarlet fever or Kawasaki disease.
- Black or hairy tongue: Black or dark-colored tongues can result from the overgrowth of bacteria or the accumulation of debris. This condition may also be caused by certain medications or poor oral hygiene.
- Pale tongue: A pale or bluish tint on the tongue can be an indication of poor blood circulation, anemia, or low oxygen levels.
While changes in tongue color are often harmless and temporary, it is important to pay attention to any persistent or concerning discoloration. If you notice abnormal color changes accompanied by other symptoms, it is best to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Difficulty Expressing Yourself and Enjoying Meals: Impact on Daily Life
Having trouble communicating effectively and savoring your meals can greatly influence your day-to-day activities and overall quality of life. In this section, we will explore the various challenges posed by difficulty speaking and eating, discussing how it can affect your personal interactions, professional engagements, and enjoyment of food.
- Struggles in Conversations
- Impairment in Work and Social Settings
- Effects on Emotional Well-being
- Decreased Nutritional Intake
- Changes in Eating Habits
- Social Isolation and Relationship Impact
First and foremost, difficulty expressing yourself verbally can lead to significant challenges in conversations and interpersonal interactions. It may affect your ability to articulate thoughts, share ideas, and engage in meaningful discussions. This can result in feelings of frustration, isolation, and potentially impact your self-confidence and social interactions.
In professional settings, people with speech difficulties may face hurdles in career advancement, as effective communication skills are often highly valued. Difficulties in conveying thoughts and ideas clearly may hinder collaboration, teamwork, and overall work performance.
The impact on emotional well-being cannot be overlooked either. Struggling to express oneself may lead to increased feelings of stress, anxiety, and low self-esteem. This can further exacerbate social challenges and result in reluctance to participate in social activities or make new connections.
Moreover, difficulties in eating can have a profound effect on your nutritional intake, potentially leading to inadequate nourishment and related health complications. Reduced ability to chew or swallow may necessitate modifications in food texture or the inclusion of soft foods, impacting the enjoyment and variety of meals.
Changes in eating habits can also disrupt the social aspect of sharing meals with friends and family. The need to adapt meals to accommodate difficulties in chewing or swallowing may result in feelings of isolation or embarrassment. This can significantly impact relationships and may lead to limited social interactions or avoidance of dining out altogether.
In summary, the challenges associated with difficulty speaking and eating extend beyond the physical aspect, impacting various aspects of daily life, including communication, work, relationships, emotional well-being, and nutritional intake. It is essential to understand these consequences and explore appropriate treatments and support to improve the overall quality of life for individuals facing such difficulties.
Treatment Options for Inflammation and Ailments of the Tongue

Once one experiences discomfort or health issues affecting the vital organ responsible for speech and taste, it becomes crucial to explore effective solutions to alleviate these problems. This section delves into various approaches and remedies that can be employed to address tongue-related infections and ensure a speedy recovery.
| Treatment | Description |
|---|---|
| Antibiotics | Prescribed medications that combat bacterial infections, promoting healing and reducing inflammation. |
| Antifungal Medications | Pharmaceutical remedies designed to eliminate fungal infections such as oral thrush. |
| Topical Ointments | Specialized creams or gels applied directly to the affected area to provide relief, reduce pain, and encourage healing. |
| Oral Rinses | Therapeutic mouthwashes that contain antimicrobial agents to cleanse the tongue and help alleviate symptoms. |
| Proper Oral Hygiene | Maintaining good dental practices such as regular brushing, flossing, and tongue scraping to prevent and manage infections. |
| Warm Saltwater Gargles | A simple yet effective remedy that involves rinsing the mouth with a warm saltwater solution to reduce inflammation and soothe discomfort. |
| Dietary Adjustments | Modifying one's diet to avoid spicy, acidic, or rough foods that may irritate the tongue and prolong the healing process. |
| Stress Management | Implementing stress-reducing techniques and lifestyle changes as stress can exacerbate tongue infections. |
It is vital to note that the specific treatment regimen may vary depending on the type and severity of the tongue infection. Therefore, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Medications and Antibiotics: Combating the Infection
In this section, we will explore the various medications and antibiotics available for effectively combating tongue infections. When it comes to addressing these types of infections, it is important to understand the role that medications play in alleviating symptoms and eradicating the underlying cause. By treating the infection promptly and appropriately, individuals can experience relief and expedite the healing process.
Medications:
Medications, such as antifungal or antiviral drugs, may be prescribed to specifically target the underlying cause of the tongue infection. These medications work by inhibiting the growth and spread of microorganisms or by directly attacking the infectious agents. It is vital to follow the prescribed dosage and complete the entire course of medication to ensure complete eradication of the infection and prevent any potential relapse.
Antibiotics:
Antibiotics are another treatment option for tongue infections caused by bacterial overgrowth. These medications are designed to combat bacterial infections by killing or inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria. Depending on the severity and nature of the infection, the healthcare provider may prescribe narrow-spectrum or broad-spectrum antibiotics. It is essential to strictly adhere to the dosage and duration of antibiotic treatment to avoid antibiotic resistance and prevent any potential side effects.
Combination Therapy:
In some cases, a combination of medications and antibiotics may be necessary to effectively combat the tongue infection. This approach is often employed when multiple microorganisms are identified as the cause of the infection or when the infection does not respond to a single type of treatment. The healthcare provider will determine the appropriate combination therapy based on the individual's specific condition and response to previous treatments.
Considerations and Precautions:
It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any medication or antibiotic treatment for a tongue infection. They will assess the underlying cause, evaluate the individual's medical history, and consider any potential drug interactions or allergies. Additionally, it is important to complete the full course of treatment as prescribed, even if symptoms improve, to ensure complete resolution of the infection. Follow-up appointments may be necessary to monitor progress and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
Home Remedies: Natural Ways to Soothe Your Oral Cavity

In this section, we will discuss various natural methods that can help alleviate discomfort in your mouth. These remedies do not involve any medical treatments and are derived from nature's gifts. By incorporating these techniques into your daily routine, you can find relief from the symptoms associated with tongue infections, such as pain, swelling, and irritation.
One effective way to soothe your tongue naturally is through the use of saltwater rinse. This simple mixture can help reduce inflammation and kill bacteria in the oral cavity. To prepare the solution, dissolve a teaspoon of salt in a cup of warm water. Gargle with the mixture for about 30 seconds, ensuring that it reaches all parts of your mouth, including your tongue. Repeat this several times a day to experience the benefits.
Another natural remedy involves the use of honey. Known for its antimicrobial properties, honey can help fight against infection-causing bacteria. Apply a small amount of raw, organic honey directly onto the affected area of your tongue. Let it sit for a few minutes before rinsing your mouth with warm water. Repeat this process a few times a day for relief from pain and soothing of the tongue.
In addition to honey, aloe vera can also provide relief for tongue infections. The gel derived from the aloe vera plant has anti-inflammatory and healing properties that can help alleviate pain and promote quicker recovery. Extract the gel from an aloe vera leaf and apply it directly onto the affected area of your tongue. Leave it for a few minutes before rinsing your mouth with water. Repeat this process multiple times daily until you notice an improvement.
Furthermore, another natural way to soothe your tongue is by consuming yogurt. The live cultures present in yogurt help restore the balance of bacteria in your mouth, preventing the overgrowth of harmful microorganisms that can cause tongue infections. Include plain, unsweetened yogurt in your diet or apply it directly onto the affected area for relief.
| Home Remedies for Soothing Your Tongue: Natural Methods |
|---|
| Saltwater rinse |
| Honey application |
| Aloe vera gel |
| Yogurt consumption or application |
FAQ
What are the common causes of tongue infections?
Tongue infections can be caused by various factors such as poor oral hygiene, smoking, dry mouth, fungal or bacterial infections, viral infections, and certain medical conditions.
What are the symptoms of a tongue infection?
Symptoms of a tongue infection may include pain or discomfort in the tongue, redness or swelling, difficulty in speaking or swallowing, changes in taste, the appearance of white patches or sores, and bad breath.
How can tongue infections be treated?
The treatment for tongue infections depends on its cause. It may include maintaining good oral hygiene, using antifungal or antibacterial medications, avoiding irritants like tobacco or spicy food, using mouth rinses or gargling with warm saltwater, and in severe cases, surgical intervention may be required.
Can tongue infections be prevented?
Yes, tongue infections can be prevented by practicing good oral hygiene, quitting smoking, staying hydrated, avoiding sharing utensils or personal items, getting timely dental check-ups, and addressing any underlying medical condition that may contribute to tongue infections.
When should I consult a doctor for a tongue infection?
It is advisable to consult a doctor if you experience persistent symptoms of a tongue infection, such as severe pain, difficulty in swallowing or speaking, high fever, or if the infection does not improve with home remedies within a few days.



