In the vast realm of nature's mysteries, one phenomenon stands as a timeless enigma: the growth and development of plants. Their ability to transform a seemingly lifeless seed into a flourishing, vibrant organism continues to captivate and enchant scientists and laymen alike. Behind the scenes of this wondrous creation lies a complex web of interdependent processes, meticulously orchestrated by nature herself. As scientists delve deeper into the secrets of plant growth, new revelations emerge, shedding light on the intricate mechanisms that govern this awe-inspiring process.
With roots firmly anchored in the soil, plants embark on a never-ending quest for nourishment, drawing sustenance from the earth's wealth. Each molecule of water, penetrating the intricate network of roots and capillaries, is a vital elixir that fuels the plant's journey towards maturity. But the journey of water through the soil is not merely a simple transaction. It is a dance of symbiosis, where the soil becomes the stage for a grand orchestration of interactions. As water cascades through the soil, relinquishing its nutrients, minerals, and moisture, a delicate balance is struck between the needs of the plant and the bounties of the earth.
However, understanding the intricacies of this intricate soil-plant relationship has proved to be a formidable challenge. But what if there is more to the story than meets the eye? What if beneath the surface of the soil, a hidden world thrives, intricately interconnected with the world of plants? The tiny microorganisms, invisible to the naked eye, play an irreplaceable role in the nourishment and growth of plants. Through an enigmatic dance of give and take, these unseen forces provide plants with essential nutrients, while simultaneously benefiting from the plant's byproducts. The symbiotic dance between plants and soil microorganisms lays bare the intricate balance of nature, highlighting the profound interconnectedness of all living beings.
The Significance of Hydration in the Development of Plants
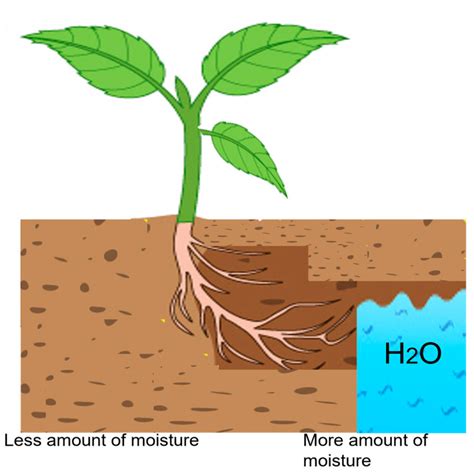
Water is a vital element in the progression and prosperity of plants. Its presence plays a crucial role in the overall growth and development of various species. Without adequate watering, plants would struggle to survive and thrive in their respective environments.
Hydration is a fundamental process that plants rely on for their sustenance and essential functions. Just like how humans need water to maintain their bodily functions, plants also require a consistent supply of water to carry out their biological processes.
Watering serves as a lifeline for plants, as it is responsible for various physiological and biochemical reactions necessary for their growth. It facilitates the transportation of nutrients and minerals through the roots, stems, and leaves of plants, enabling them to perform photosynthesis, produce essential compounds, and develop sturdy structures.
Moisture acts as a catalyst for cellular expansion and elongation, allowing plants to generate new tissues and ultimately increase their size and volume. It supports the metabolism of plants, ensuring the efficient absorption and utilization of nutrients from the soil.
In addition to nourishing plants, watering also helps in regulating their temperature through transpiration. This process involves the release of water vapor from the leaves, thereby cooling the plant and preventing overheating.
The art of watering lies in striking a balance between providing enough moisture for optimal growth and avoiding excessive water that can lead to root rot and other detrimental conditions. Understanding the water requirements of different plant species and adjusting watering schedules accordingly is vital for their long-term health and sustainability.
Whether through natural rainfall or manual irrigation, consistent watering practices are directly linked to the successful cultivation of plants, ensuring they bloom and bear fruits to their fullest potential.
Understanding the Role of Soil in Plant Development
Delving into the intricate mechanisms of plant growth, an exploration of the vital role of soil emerges. Harnessing the power of nature's elements, soil acts as the foundation for plant development, nurturing and supporting life in a symbiotic relationship. The significance of soil in the growth and prosperity of plants goes beyond surface-level observation, unveiling a complex interplay of nutrients, moisture, and microorganisms.
Roots Anchored in Nutrient-Rich Soil: Akin to a nutrient reservoir, soil provides plants with essential elements required for optimal growth and development. As roots extend deep into the soil, they encounter a complex matrix of organic matter, minerals, and microorganisms, forming a conducive environment for nutrient absorption. The quality and composition of the soil play a pivotal role in the availability of nutrients to the plants, influencing their overall vitality and productivity.
A Moisture Oasis for Plant Life: Like an oasis in the desert, soil holds the key to the hydration needs of plants. Its ability to retain and release water enables plants to withstand periods of drought and regulate their water intake. Moist soil creates a hospitable environment for the roots to access water, facilitating nutrient transport and metabolic processes crucial for plant growth. The delicate balance between water retention and drainage in the soil contributes significantly to the optimization of plant development.
A Microbial Community Fueling Growth: Beneath the surface of the soil lies a bustling ecosystem of microorganisms, often unnoticed but essential for plant development. These microscopic organisms, including bacteria, fungi, and protozoa, engage in a myriad of symbiotic relationships with plants, aiding nutrient uptake, enhancing soil structure, and protecting against diseases. These unseen allies contribute to a healthy and thriving soil environment, fostering the growth and resilience of plants.
A Foundation for Plant Prosperity: Soil serves as the foundation upon which the intricate symphony of plant development is orchestrated. From the provision of essential nutrients to the facilitation of water absorption and the promotion of microbial interactions, the role of soil is multifaceted and indispensable. Understanding the complex dynamics and interdependencies within the soil-plant relationship unravels the secrets of successful plant growth, paving the way for enhanced agricultural practices and increased environmental sustainability.
The Science of Effective Hydration Techniques

Understanding the principles behind adequate hydration methods is crucial for nurturing the optimal growth and development of plants. Through a comprehensive analysis of scientific research and experiments, this section aims to shed light on the intricate processes involved in effectively providing plants with the water they need to thrive.
Gaining insights into optimal hydration techniques
Proper hydration techniques are not solely reliant on the quantity of water plants receive, but also on the quality and timing of irrigation. By exploring the biological mechanisms that regulate water absorption and transpiration in plants, we can unlock the secrets to achieving healthy growth and vibrant foliage.
The role of water in cellular processes
Water plays a vital role in a multitude of cellular processes within plants, including photosynthesis, nutrient uptake, and transportation of essential compounds. By understanding how water molecules interact with various plant tissues and cells, we can design watering techniques that foster efficient nutrient absorption and distribution.
Optimizing irrigation strategies
Developing the optimal irrigation strategy involves balancing the water requirements of the plants with the environmental conditions and growth stage. We delve into the factors that affect plant water needs, such as temperature, humidity, soil type, and root structure, to help you tailor your watering schedule and methods accordingly.
Preventing water-related plant stress
Overwatering or underwatering can lead to detrimental effects on plant health, such as root rot, nutrient deficiencies, and stunted growth. By delving into the signals that indicate water stress and the physiological responses of plants to water scarcity or excess, we provide insights into identifying and rectifying watering patterns that may be compromising plant vitality.
Maintaining an optimal watering routine
Establishing a consistent and well-balanced watering routine is essential for sustaining long-term plant health. We discuss best practices for assessing soil moisture levels, determining watering frequency, and implementing irrigation methods that promote deep root growth and overall vegetative vigor.
Conclusion
By delving into the science behind proper watering techniques, you will gain a deeper understanding of the intricate balance between hydration, plant physiology, and optimal growth. Armed with this knowledge, you can establish a nurturing environment that supports the flourishing of your plants and unlocks their full potential.
Exploring Various Irrigation Techniques for Optimal Plant Development
Within the realm of enhancing plant growth, an exploration of diversified watering methods proves to be an indispensable endeavor. By delving into the diverse possibilities of irrigation techniques, researchers ambitiously strive to foster the ideal conditions for plants' thriving development. This section seeks to shed light on the significance and efficiency of different watering techniques, highlighting their potential contributions to the overall growth and vitality of plants.
| Watering Method | Description | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Drip Irrigation | Employing a network of tubes and emitters, this technique delivers water directly to the base of plants, efficiently minimizing water wastage. | - Conserves water - Provides precise control over irrigation - Reduces risk of foliage diseases |
| Sprinkler Irrigation | Using an overhead system of nozzles, this method simulates rainfall by spreading water uniformly across the garden. | - Ensures even distribution of water - Promotes larger root systems - Aids in combating pests and diseases |
| Soaker Hoses | These porous hoses seep water directly into the soil, promoting deep root growth and reducing evaporation rates. | - Conserves water through minimal runoff - Prevents weed growth through precise application - Enhances root development |
| Surface/Flood Irrigation | With this technique, water is distributed across the soil surface, allowing for efficient absorption by plant roots. | - Distributes nutrients evenly in the soil - Suitable for large-scale irrigation - Enhances soil fertility |
| Sub-Irrigation | In this method, water is delivered to plants from below by utilizing a reservoir or a sub-irrigation system. | - Reduces water evaporation - Prevents weed growth - Provides direct hydration and nutrient uptake |
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of these varied irrigation techniques, gardeners and agricultural professionals can make informed decisions regarding the most suitable watering method for their specific plant species and gardening scenarios. Furthermore, by optimizing the irrigation process, the overall health and productivity of plants can be maximized, fostering a flourishing environment for lush vegetation and bountiful harvests.
Factors Influencing Water Uptake in Plants
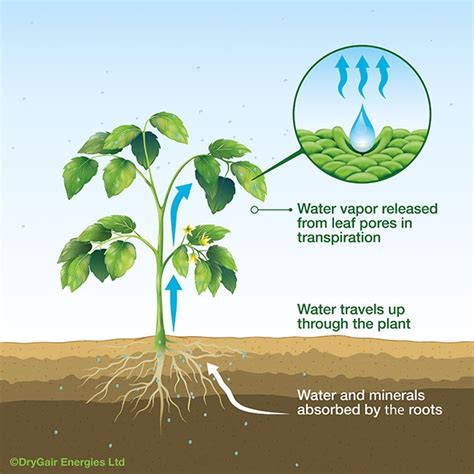
Understanding the various elements that impact the absorption of water by plants is crucial for comprehending their growth and development. Numerous factors interact in a complex manner to regulate the uptake of water in plants. This section delves into the critical aspects that influence the process of water absorption, shedding light on the intricate mechanisms that ensure plants receive adequate moisture for their survival.
The Connection Between Soil Moisture and Nutrient Absorption
Understanding the intricate relationship between the moisture content of soil and the ability of plants to absorb essential nutrients is a crucial aspect of unraveling the mysteries of plant growth. Proper moisture levels in the soil play a pivotal role in facilitating the uptake of vital elements by plants.
Soil moisture, often described as the amount of water held in the soil, acts as a lifeline for plants, influencing their ability to acquire and absorb nutrients. It serves as a conduit for the transport of minerals from the soil to the roots, enabling plants to sustain healthy growth and development.
When the soil moisture content is optimal, it creates a favorable environment for nutrient uptake, allowing plants to access the essential elements they require for various physiological processes. Adequate soil moisture ensures that water-soluble nutrients dissolve and move freely through the soil, making them readily available for plant roots to absorb.
The interplay between soil moisture and nutrient uptake is a delicate balance. Insufficient moisture levels can hinder the movement of nutrients, impeding their accessibility to plants. On the other hand, excessive soil moisture can lead to waterlogging, which creates oxygen-deprived conditions that impede root functioning and nutrient absorption.
In addition to facilitating nutrient absorption, adequate soil moisture also contributes to plant health in other ways. It helps maintain turgor pressure, which gives plants firmness and rigidity, enabling them to stand upright. Furthermore, proper moisture levels aid in regulating temperature within the plant, preventing overheating and subsequent stress.
Recognizing the critical role of soil moisture in nutrient uptake and plant growth highlights the significance of understanding and managing soil moisture levels. By implementing effective watering strategies and ensuring optimal soil moisture, gardeners and farmers can unlock the full potential of their crops, leading to healthier and more abundant yields.
Recognizing Signs of Insufficient and Excessive Moisture Levels in Plants

Within the realm of nurturing plant growth and ensuring their well-being, one crucial aspect to be mindful of is maintaining an appropriate balance of water intake. Proper hydration is vital for plants to thrive, as both insufficient and excessive moisture can have detrimental effects on their health. By being aware of the signs that indicate plants are either underwatered or overwatered, gardeners and plant enthusiasts can proactively address these issues to optimize the growth and vitality of their green companions.
The symptoms of underwatering can vary, but often include visibly dry soil, wilting and drooping leaves, and a general lack of vibrancy in the plant's appearance. In contrast, overwatering manifests in different ways, such as yellow or browning leaves, root rot, and an excessive amount of moisture in the soil. It is essential to be able to identify these signs promptly, as they can serve as valuable indicators of the plant's hydration needs.
- Wilting and drooping leaves
- Dry soil that is hard to the touch
- Stunted growth or lack of new leaves
- Yellowing or browning of leaves
- Root rot or a foul odor from the soil
When plants are underwatered, their soil becomes dry and parched, akin to a desert's arid terrain. The leaves lose their turgidity, resulting in a withered and wilted appearance. In contrast, plants that are overwatered experience a suffocating surplus of moisture that impedes healthy root development and leads to the stagnation of growth. Understanding and recognizing these signs is crucial for maintaining the optimal moisture balance in plants, helping them thrive and reach their full potential.
By closely observing their plants and being attentive to subtle changes in appearance and behavior, gardeners can easily detect signs of both underwatering and overwatering. Regularly assessing the moisture content of the soil, incorporating appropriate watering techniques, and adjusting watering schedules accordingly are effective strategies to prevent these imbalances and foster healthy plant growth.
Strategies for Conserving Water in Plant Care
Enhancing water conservation is crucial when it comes to nurturing plants and ensuring their optimal growth. In this section, we will explore various approaches and techniques that can be employed to minimize water consumption while still maintaining the health and vitality of your plants.
1. Efficient Irrigation: Employing efficient irrigation systems and practices is paramount in conserving water. Drip irrigation, for instance, delivers water directly to the root zone, reducing evaporation and runoff. Additionally, using timers and sensors helps to ensure that plants receive water only when necessary, preventing over-watering.
2. Mulching: Applying a layer of organic mulch around your plants can significantly improve water conservation. Mulch acts as a barrier, reducing evaporation and maintaining soil moisture levels. Moreover, it helps to prevent the growth of weeds, which compete with your plants for water and nutrients.
3. Proper Plant Selection: Choosing plants that are well-suited to your climate and soil conditions can enhance water conservation. Native plants and those with drought-resistant qualities require less water to thrive, reducing the overall water demand in your garden.
4. Watering Techniques: Implementing proper watering techniques can enhance water conservation. Water deeply and infrequently, allowing the soil to dry out between watering sessions. This approach encourages plants to develop deep and robust root systems, enabling them to access water from lower soil layers.
5. Soil Health: Maintaining optimal soil health is crucial in conserving water. Amending soil with organic matter improves its ability to retain moisture, reducing the frequency of watering. Furthermore, aerating the soil promotes better water infiltration and prevents surface runoff.
6. Reusing and Collecting Water: Implementing measures to reuse and collect water can contribute to water conservation efforts. Collect rainwater using barrels or tanks, which can then be used to irrigate plants. Utilize household greywater, after appropriate treatment, to provide additional hydration to your plants.
By incorporating these strategies into your plant care routine, you can contribute to water conservation efforts, promote a sustainable gardening approach, and ensure the long-term health and vitality of your plants.
Tips for Achieving Optimal Growth of Plants through Effective Watering Techniques

In this section, we will discuss some valuable insights into achieving the best possible plant growth by employing proper watering methods. Watering is an essential aspect of cultivation, and understanding how to water plants appropriately can significantly impact their overall health and development.
1. Understand the Watering Needs of Different Plant Species
It is vital to recognize that different plants have varying water requirements. Some plants thrive in moist conditions, while others prefer a drier environment. Therefore, familiarize yourself with the watering needs of your specific plant species to provide adequate moisture without overwatering.
2. Water Deeply and Infrequently
Instead of giving plants small amounts of water throughout the day, it is generally more beneficial to water the plants deeply and infrequently. This technique ensures that the water reaches the roots, encouraging the plants to develop deep root systems that can access water and nutrients more efficiently.
3. The Importance of Proper Drainage
Ensuring good drainage is crucial when watering plants. If the water does not drain effectively, the roots may become waterlogged, leading to root rot and other harmful conditions. Opt for well-draining soil and use planters or containers with drainage holes to prevent water from stagnating.
4. Timing is Key
Timing your watering sessions appropriately can be advantageous for plant growth. Watering early in the morning allows the plants to absorb moisture before the sun's heat increases, preventing excessive evaporation. Similarly, evening watering helps plants replenish their water content overnight.
5. Avoid Overwatering
Overwatering is a common mistake that can hinder plant growth. It is essential to strike a balance between providing enough water and avoiding excessive moisture. Regularly check the soil's moisture level before watering, and ensure the top inch of soil is slightly dry before watering again.
6. Mulching for Water Retention
Applying a layer of organic mulch around the plants can help retain moisture in the soil, reducing the frequency of watering. Mulch acts as a barrier, preventing evaporation and keeping the soil moist for longer periods.
7. Watering Techniques for Different Seasons
Adjust your watering techniques based on the seasons. Plants have different water requirements during hot summer months compared to cooler winter periods. Pay attention to weather changes and adapt your watering routine accordingly.
By implementing these tips for proper watering techniques, you can optimize the growth of your plants, ensuring their vitality and longevity. Remember to monitor your plants closely, as their watering needs may change during different stages of growth and in response to environmental factors.
FAQ
Why is watering soil important for plant growth?
Watering soil is important for plant growth because water is essential for plant cells to carry out crucial biochemical processes such as photosynthesis, transpiration, and nutrient uptake. It helps in the absorption of nutrients from the soil and their transportation to different parts of the plant. Additionally, water maintains turgidity in plant cells, which supports their structure and allows plants to stand upright.
How often should I water my plants?
The frequency of watering plants depends on various factors such as the type of plant, its stage of growth, the temperature, and humidity of the environment, as well as the type of soil. Generally, most plants perform best with regular watering when the top inch of soil becomes dry. However, it is important to avoid overwatering as it can lead to root rot and other fungal infections.
What are the signs of overwatering plants?
The signs of overwatering plants include yellowing or wilting leaves, drooping stems, moldy or mushy soil, and the presence of fungus gnats or other pests. Overwatering restricts the availability of oxygen to the plant roots, causing them to rot and become susceptible to diseases. Therefore, it is crucial to strike a balance and provide adequate water without drowning the plants.
Can plants survive without watering?
While some plants have adaptations that allow them to survive extended periods without water, most plants require a sufficient water supply for optimal growth. Water is vital for the process of photosynthesis, which converts sunlight into energy for the plant. Without water, plants can become dehydrated, wilt, and eventually die. Therefore, regular watering is essential for their survival.
Are there any alternative methods for watering plants besides using water from the tap?
Yes, there are alternative methods for watering plants besides using tap water. Rainwater harvesting systems, greywater reuse, and drip irrigation are some popular methods. Rainwater can be collected in barrels or tanks and then used to water plants. Greywater, which is the relatively clean wastewater from household activities, can also be used for irrigation after appropriate treatment. Drip irrigation systems provide water directly to the roots, minimizing wastage and promoting efficient water use.
How does watering soil affect plant growth?
Watering soil is essential for plant growth as it provides the necessary hydration for plants to perform their vital functions such as photosynthesis, nutrient uptake, and cell expansion. Watering helps maintain the turgor pressure in plant cells, allowing them to remain firm and upright. It also aids in the transport of nutrients from the soil to different parts of the plant. Without proper watering, plants may suffer from wilting, nutrient deficiencies, and stunted growth.



