With the advent of numerous modern ailments plaguing humanity, there is one insidious predator that silently lurks beneath the surface - a formidable adversary that stealthily encroaches upon our body's largest organ, leaving devastation in its wake. This enigmatic nemesis, often whispered about in hushed tones, is the subject of much concern and curiosity - a force to reckon with known as skin cancer.
By delving deeper into the realms of dermatological mysteries, we uncover a web of causes and triggers that set the stage for this malignant intruder. Understanding the intricacies that contribute to the development of this formidable illness is vital in our quest for prevention and protection. Through knowledge, we arm ourselves against the shadowy embrace of skin cancer's encompassing grip.
This somber lyricism of skin cancer's narrative finds its crescendo in the myriad of symptoms it presents. Though elusive in nature, this treacherous disease manifests itself through a myriad of signs that can be both striking and subtle. It is through keen observation and an understanding of these telltale markers that we can recognize the enemy within, allowing us to take decisive action in the face of impending danger.
In our pursuit of safeguarding ourselves from the lurking menace of skin cancer, we must become the architects of our own defense. Armed with invaluable insights and a multifaceted arsenal of preventive measures, we can erect barriers against this silent predator. Through diligent sun protection, early detection, and lifestyle modifications, we empower ourselves to tilt the scales in our favor, ensuring that the darkness of skin cancer remains a distant specter in our lives.
Understanding Skin Cancer: The Causes, Symptoms, and Ways to Prevent It
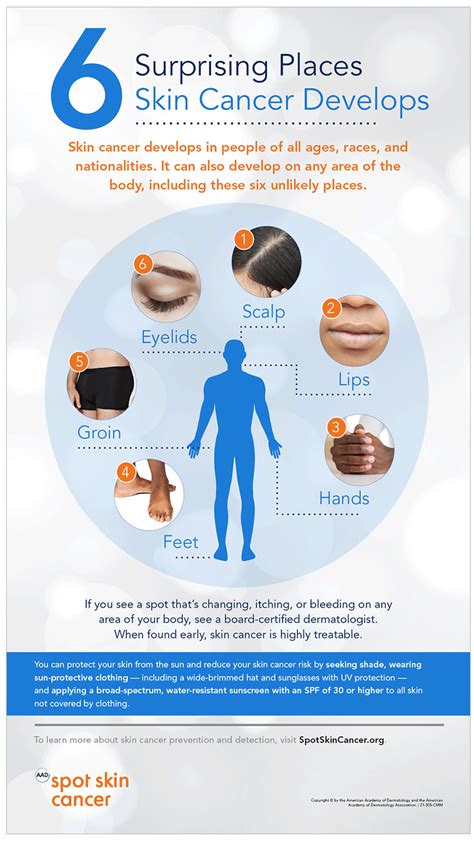
In this section, we will delve into a comprehensive understanding of skin cancer, exploring the factors that contribute to its development, the signs and symptoms to watch out for, and effective strategies to prevent its occurrence. Skin cancer is a serious health condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. By gaining insight into its causes, recognizing its symptoms, and implementing preventive measures, we can empower ourselves to protect our skin and reduce the risk of developing this potentially life-threatening disease.
Causes of Skin Cancer |
To comprehend the causes of skin cancer, we need to examine the various risk factors associated with its development. Excessive and unprotected exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun, frequent use of tanning beds, a history of sunburns, and having fair skin, light-colored hair, and blue or green eyes all contribute to an increased susceptibility to skin cancer. Additionally, genetic predisposition, a weakened immune system, and certain medical conditions or treatments can also play a role in its onset. |
Symptoms of Skin Cancer |
Skin cancer presents itself in various forms, with certain common symptoms that indicate its presence. These may include the development of new moles or growths on the skin, changes in the appearance of existing moles, such as irregular borders, uneven colors, or growth in size, and sores that do not heal or bleed easily. It is crucial to remain vigilant and seek medical attention promptly if any suspicious changes on the skin are noticed, as early detection and treatment can significantly increase the chances of successful recovery. |
Prevention of Skin Cancer |
The prevention of skin cancer involves adopting proactive measures to minimize exposure to harmful UV radiation and protect the skin. Wearing sunscreen with a high Sun Protection Factor (SPF), seeking shade during peak sun hours, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding the use of tanning beds are all crucial steps in safeguarding the skin against potential damage. Regular skin self-examinations and annual visits to a dermatologist are also vital for early detection and treatment if cancerous changes are detected. By implementing these preventive strategies, we can take control of our skin health and reduce the risk of developing skin cancer. |
The Basics: What is Skin Cancer?
Understanding the fundamental concept of skin cancer is crucial in order to effectively address this life-threatening condition. Skin cancer, a malignant disease, affects the body's largest organ, the skin. It is characterized by the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells that can spread and invade nearby tissues and organs.
There are different types of skin cancer, with the most common ones being basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. Basal cell carcinoma primarily affects the basal cells, which are located in the deepest layer of the epidermis. Squamous cell carcinoma, on the other hand, develops in the squamous cells, which form the upper layers of the skin. Melanoma, the most aggressive form of skin cancer, originates from melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing the pigment melanin.
While the exact causes of skin cancer are not fully understood, several risk factors have been identified. Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds is a significant contributing factor. Other risk factors include having fair skin, a history of sunburns, family history of skin cancer, a weakened immune system, and exposure to certain chemicals and substances.
Recognizing the symptoms of skin cancer is crucial for early detection and treatment. Common signs include changes in the appearance of moles or growths, the development of new growths or sores that do not heal, itching or tenderness in a mole or lesion, and changes in the color, size, or shape of a mole.
Prevention is key in reducing the risk of skin cancer. This can be achieved by practicing sun safety measures such as wearing sunscreen with a high SPF, seeking shade, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding the use of tanning beds. Regular self-examinations and annual skin screenings by a dermatologist are also essential in detecting skin cancer at its early stages.
| Type of Skin Cancer | Origin |
|---|---|
| Basal Cell Carcinoma | Basal cells in the deepest layer of the epidermis |
| Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Squamous cells in the upper layers of the skin |
| Melanoma | Melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin |
Types of Cutaneous Melanoma and Their Characteristics
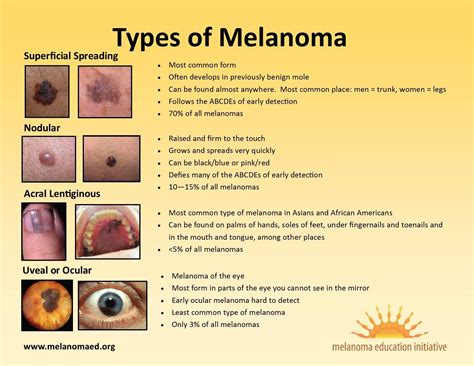
In this section, we will explore the different varieties of cutaneous melanoma and discuss their distinctive features. Understanding the various types of skin cancer can help in detecting and diagnosing the condition at an early stage, enabling timely treatment and improving outcomes.
| Type of Skin Cancer | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Superficial Spreading Melanoma | This type of melanoma typically appears as irregularly-shaped patches with varying shades of brown, black, or tan. It tends to grow horizontally at first before penetrating deeper into the skin. |
| Nodular Melanoma | Nodular melanoma is characterized by a raised, round bump on the skin that can be black, blue, brown, or red in color. It often grows at a faster rate compared to other types of melanoma. |
| Lentigo Maligna Melanoma | Lentigo maligna melanoma typically develops on areas of skin exposed to the sun over many years, such as the face and neck. It usually appears as a large, flat lesion with uneven borders and varying shades of brown. |
| Acral Lentiginous Melanoma | This type of melanoma is commonly found on the palms of the hands, soles of the feet, or under the nails. It may resemble a bruise or a dark streak and is often diagnosed at an advanced stage due to its hidden location. |
| Amelanotic Melanoma | Amelanotic melanoma is characterized by the absence of pigment, making it difficult to identify. It can resemble other skin conditions, such as eczema or a pimple, and is often misdiagnosed or overlooked. |
Being familiar with the different types of cutaneous melanoma can assist individuals in recognizing potential warning signs and seeking professional medical advice. Early detection and proper treatment are crucial in effectively managing skin cancer and improving overall prognosis.
Sun Exposure: The Primary Factor Behind Skin Cancer
When it comes to the development of skin cancer, one undeniable culprit stands out above the rest: sun exposure. The rays emitted by the sun contain harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation that penetrates the skin, triggering various detrimental effects that can pave the way for the formation of cancerous cells.
It is essential to comprehend the significance of protecting oneself from excessive sun exposure in order to ensure a reduced risk of developing skin cancer. Understanding the causes and consequences of sun exposure can serve as a crucial starting point in implementing effective preventive measures.
- UV Radiation: Ultraviolet radiation, including UVA and UVB rays, emitted by the sun is the primary cause of skin cancer. These rays have the ability to damage the DNA in skin cells, ultimately leading to abnormal cell growth and the formation of cancerous tumors.
- Intense Sunlight: Prolonged exposure to intense sunlight, especially during peak hours between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., increases the risk of skin cancer. It is recommended to seek shade or limit outdoor activities during these times to minimize exposure.
- Tanning Beds: Artificial sources of UV radiation, such as tanning beds, contribute to the risk of developing skin cancer. The concentrated UV radiation emitted by tanning beds can cause significant damage to the skin, making it vital to avoid their use.
- Geographical Location: Individuals living in regions closer to the equator or at higher altitudes are exposed to more intense UV radiation due to the angle of the sun's rays. Therefore, increased caution and diligence are crucial in these areas.
- Skin Type: Individuals with fair skin that burns easily or tans minimally are more susceptible to the harmful effects of the sun. Having a naturally darker complexion does not provide complete protection either, making sun safety essential for everyone.
Protecting oneself from sun exposure is paramount in reducing the risk of skin cancer. This includes the consistent and proper use of sunscreen with a high SPF, wearing protective clothing that covers the skin, donning sunglasses and hats to shield the face and eyes, and seeking shade whenever possible.
Understanding the leading cause of skin cancer, which is excessive sun exposure, empowers individuals to make informed decisions regarding their sun protection habits. By taking proactive measures, one can significantly decrease the chances of developing this potentially life-threatening disease.
Understanding UV Radiation and its Harmful Effects
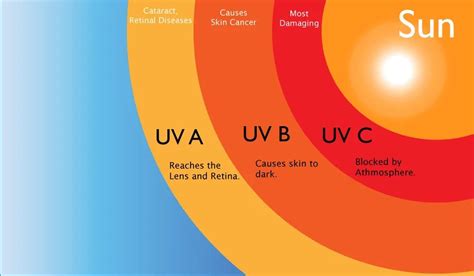
Exploring the intricate link between exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation and the detrimental impact on our skin is crucial for comprehending the risks associated with prolonged sun exposure. The enigmatic nature of UV radiation highlights the need for a comprehensive understanding of its harmful effects on our bodies.
The Power of UV Radiation
UV radiation, a potent form of electromagnetic radiation, inherently possesses the ability to profoundly affect the human body. This type of radiation consists of three distinct categories: UVA, UVB, and UVC rays. While UVA rays penetrate the deepest layers of the skin, contributing to premature aging, UVB rays are primarily responsible for sunburns and can potentially lead to skin cancer. UVC rays, on the other hand, are absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere and do not pose a direct threat to our skin.
The Impact on Skin Health
When our skin is exposed to excessive amounts of UV radiation, it undergoes significant changes. The DNA within our skin cells becomes damaged, hindering their ability to function properly and potentially leading to the development of skin cancer. Long-term exposure to UV radiation can also expedite the aging process, resulting in the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and age spots.
Shielding Against Harmful UV Rays
Preventing the detrimental effects of UV radiation on our skin requires adopting proactive sun protection measures. Applying broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF value, wearing protective clothing, such as wide-brimmed hats and long-sleeved shirts, and seeking shade during peak sun hours are essential steps towards mitigating the risks associated with UV radiation. Regular skin examinations and self-checks also play a crucial role in early detection and prevention of skin cancer.
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the nature of UV radiation and its detrimental effects on our skin, we empower ourselves to take the necessary precautions to protect our skin health and reduce the risk of developing skin cancer.
The Role of Genetics in the Development of Cutaneous Carcinoma
Genetics plays a significant role in the susceptibility and development of skin cancer. Numerous studies have indicated that certain genetic factors influence an individual's likelihood of developing this condition. Understanding the interplay between genes and skin cancer can provide valuable insights into disease prevention and early detection.
- 1. Inherited Genetic Mutations:
- 2. Familial Risk Patterns:
- 3. Genetic Variations and Sun Sensitivity:
- 4. Role of Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes:
- 5. Personalized Prevention and Interventions:
Some individuals inherit specific genetic mutations that increase their vulnerability to skin cancer. Mutations in genes such as CDKN2A and TP53 have been linked to an increased risk of developing cutaneous carcinoma. These genetic aberrations impair the body's ability to suppress tumor formation, making affected individuals more susceptible to skin cancer.
Family history also plays a crucial role in determining an individual's likelihood of developing skin cancer. Individuals with a close relative, such as a parent or sibling, who has been diagnosed with skin cancer, are at a higher risk of developing the disease themselves. This suggests that there may be inherited genetic factors at play, contributing to familial clusters of cutaneous carcinoma.
Genetic variations can influence an individual's sensitivity to UV radiation, a significant risk factor for skin cancer development. Certain gene variants affect the production and repair of DNA damaged by UV radiation, rendering some individuals more susceptible to malignancies caused by excessive sun exposure.
Oncogenes are genes that, when mutated, can promote the uncontrolled growth of skin cells, leading to tumor formation. Conversely, tumor suppressor genes are responsible for regulating cell growth and preventing the development of cancer. Genetic alterations in these oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes can significantly impact an individual's susceptibility to skin cancer.
Understanding the genetic factors involved in skin cancer development can pave the way for personalized prevention strategies and interventions. Genetic testing can help identify individuals with an increased risk, allowing for targeted and proactive measures such as regular skin screenings, sun protection education, and tailored treatment plans.
By unraveling the intricate relationship between genetics and skin cancer development, researchers and healthcare professionals aim to develop more effective prevention strategies and personalized treatment approaches, ultimately reducing the burden of this potentially deadly disease.
Risk Factors: Who is at Higher Risk for Developing Skin Cancer?

When it comes to the prevalence of skin cancer, certain individuals are at a higher risk than others. Although skin cancer can affect anyone, understanding the factors that increase the likelihood of developing this condition can aid in early detection and proactive prevention.
1. Fair Skin: People with fair skin, particularly those who burn easily and have light hair and eye color, have a higher risk of developing skin cancer. This is because fair skin has less natural protection against harmful UV radiation.
2. Sun Exposure: Prolonged exposure to the sun's ultraviolet (UV) rays increases the risk of skin cancer. Individuals who spend a significant amount of time outdoors, whether for work or leisure, without adequate protection are more susceptible.
3. History of Sunburns: A history of severe sunburns, especially during childhood or adolescence, can increase the risk of developing skin cancer later in life. It is important to protect the skin from sunburns, as they can cause lasting damage to skin cells.
4. Family History: If a close family member has had skin cancer, such as a parent or sibling, the risk of developing the condition is higher. This suggests a potential genetic predisposition to skin cancer and should be taken into consideration.
5. Age: As individuals age, their risk of developing skin cancer increases. This can be attributed to cumulative exposure to UV radiation over time and a decrease in the skin's ability to repair itself.
6. Weakened Immune System: People with weakened immune systems, whether due to certain medications, medical conditions, or organ transplants, have an elevated risk of developing skin cancer. A weakened immune system may be less capable of detecting and controlling abnormal cell growth.
7. Certain Types of Skin Conditions: Some skin conditions, such as actinic keratosis, xeroderma pigmentosum, and basal cell nevus syndrome, are associated with a higher risk of developing skin cancer. These conditions can cause DNA damage and impair the skin's ability to repair itself.
It is important to note that having one or more risk factors does not guarantee the development of skin cancer. However, individuals with these risk factors should prioritize regular skin examinations, sun protection measures, and be vigilant in identifying any changes or abnormalities on their skin.
Recognizing Common Indicators and Early Signals of Skin Cancer
Identifying the warning signs and symptoms of skin cancer is crucial in promoting early detection and effective treatment. Being aware of the common indications of this condition can empower individuals to take necessary precautions and seek medical attention promptly.
When it comes to skin cancer, there are several visible markers that can serve as red flags. These include changes in the size, shape, or color of moles or freckles, the development of new sores or growths, or any persistent itching, tenderness, or pain in certain areas of the skin.
- Moles or freckles: Observe any moles or freckles on your skin for any alterations in their appearance. Look out for moles that are asymmetrical, have irregular borders, exhibit variations in color, or are larger than a pencil eraser.
- New sores or growths: Keep an eye on any newly-formed sores, growths, or lumps that do not heal within a reasonable timeframe. These may bleed or crust over, causing discomfort or presenting a persistent scaly or rough texture.
- Itching, tenderness, or pain: Notice any frequent itching, tenderness, or pain in particular areas of your skin. These sensations may indicate an underlying issue that requires attention, especially if they persist or worsen over time.
Routine self-examinations of your skin can significantly contribute to the early detection of potential skin cancer. By familiarizing yourself with your individual skin characteristics and monitoring any changes, you can promptly address any concerning symptoms with a healthcare professional.
Remember, being proactive in recognizing the common symptoms and early warning signs of skin cancer is essential in preserving your health and well-being. If you notice any persistent or unusual changes in your skin, consult a dermatologist for a comprehensive evaluation and appropriate treatment options.
Take Action: Preventing the Onset of Skin Cancer

Empower yourself with knowledge and actionable steps to significantly reduce the risk of developing skin cancer. By adopting preventive measures and taking proactive steps in your daily routine, you can safeguard your skin against this potentially life-threatening condition.
- 1. Shield your skin from harmful UV rays: Limit your direct exposure to the sun, especially during peak hours when the sun's rays are the strongest. Seek shade, wear protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts and wide-brimmed hats, and use sunscreen with a high SPF regularly.
- 2. Perform regular self-examinations: Conduct routine self-checks to monitor the condition of your skin. Familiarize yourself with the ABCDE rule, which includes looking out for Asymmetry, irregular Borders, a variation in Color, a Diameter larger than 6 millimeters, and Evolving or changing characteristics of moles or skin lesions.
- 3. Encourage healthy sun-safe practices in children: Educate children about the importance of sun protection and instill good habits from an early age. Teach them to seek shade, wear protective clothing, and apply sunscreen regularly.
- 4. Avoid tanning beds and sunlamps: Steer clear of artificial tanning methods, as they can cause significant damage to your skin and increase the risk of skin cancer. Embrace your natural skin tone and opt for sunless tanning alternatives, like self-tanning lotions or sprays.
- 5. Stay vigilant and seek professional help: Regularly visit a dermatologist for skin check-ups and screenings, especially if you have a family history of skin cancer or notice any concerning changes in your skin's appearance or texture. Early detection plays a crucial role in successful treatment outcomes.
- 6. Spread awareness and promote sun-safe practices: Share your knowledge with friends, family, and community members to create a collective effort in preventing skin cancer. Advocate for the implementation of sun protection measures in schools, workplaces, and public spaces to ensure a sun-safe environment for everyone.
By following these preventive measures and engaging in proactive habits, you can make a significant difference in reducing the risk of skin cancer and promoting optimal skin health. Remember, prevention is key when it comes to protecting your skin from the potential harm caused by sun exposure and other risk factors associated with skin cancer.
Regular Skin Checks: Early Detection of Skin Cancer
In the quest to safeguard our skin health, it is essential to prioritize regular skin examinations. By devoting time to examine our skin thoroughly, we can potentially detect any signs of skin cancer in its early stages. These routine checks play a crucial role in identifying any abnormalities or changes in the skin that may require further medical attention.
Conducting regular skin examinations not only creates awareness about the overall condition of our skin but also aids in the early detection of potential skin cancer. By examining every inch of our skin, we can become proactive in identifying any irregularities, such as new moles, growths, or changes in existing moles. Early detection increases the chances of successful treatment and can significantly improve the prognosis for individuals diagnosed with skin cancer.
To ensure thorough skin examinations, it is advisable to follow a systematic approach. Starting from the head and moving down to the toes, one can carefully observe the skin's color, texture, and any visible irregularities. Paying close attention to areas that are frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck, arms, and legs, is particularly important. Using a mirror or seeking the assistance of a partner can aid in examining hard-to-reach areas effectively.
- Inspect the face, including the nose, lips, mouth, and ears, carefully.
- Examine the scalp, using a comb or hairdryer to separate the hair and look for any concerning spots or moles.
- Check the neck, both front, and back, along with the upper chest area.
- Thoroughly evaluate the arms, including the elbows, underarms, and hands.
- Pay attention to the lower torso, examining the chest, abdomen, and genital area.
- Move on to the legs, checking the thighs, knees, calves, and feet, including the soles and toenails.
It is important to keep a record of any findings during these examinations. This allows for ongoing monitoring and comparison of any changes or developments in the skin over time. Should any concerning symptoms or alterations be noticed, it is crucial to promptly consult with a dermatologist or medical professional for further evaluation and guidance.
Regular skin examinations serve as a proactive measure in the early detection of skin cancer. By dedicating time to carefully observe and evaluate our skin, we can play an active role in maintaining our overall skin health and potentially identify any concerning abnormalities before they progress.
Sunscreen and Sun-Safe Practices: Protecting Your Skin

Ensuring the health of our skin under the sun's powerful rays is of utmost importance. In this section, we will explore various ways to safeguard our skin from potential harm caused by prolonged or excessive sun exposure. By following sun-safe practices and incorporating sunscreen into our daily routine, we can significantly reduce the risk of skin damage and maintain a healthy complexion.
The Role of Sunscreen:
Sunscreen plays a crucial role in shielding our skin from the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation. UV rays, specifically UVA and UVB, have the potential to penetrate the skin's layers and cause sunburns, premature aging, and even skin cancer. By applying sunscreen with a broad-spectrum SPF (Sun Protection Factor) of 30 or higher, we can create a protective barrier that filters out these harmful rays and minimizes their impact on our skin.
Choosing the Right Sunscreen:
With the plethora of sunscreen options available in the market, it is essential to select a product that caters to our specific needs and skin type. Consider opting for a sunscreen that is labeled as "broad-spectrum," indicating that it offers protection against both UVA and UVB rays. Additionally, choose a sunscreen with an SPF appropriate for your anticipated sun exposure, whether it be for everyday activities or prolonged outdoor activities. Remember to reapply sunscreen at regular intervals, especially after swimming or excessive sweating, to maintain its effectiveness.
Sun-Safe Practices:
Aside from using sunscreen, adopting sun-safe practices can further safeguard our skin from the sun's harmful effects. Seek shade when the sun is at its peak, typically between 10 am and 4 pm, to minimize direct exposure. Wearing protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts, wide-brimmed hats, and UV-blocking sunglasses, can provide an extra layer of defense against UV rays. It is also essential to remember that even on cloudy or overcast days, UV rays can still cause damage, so practicing sun-safe habits consistently is paramount.
Conclusion:
Prioritizing the protection of our skin against the potential harm caused by sun exposure is vital for maintaining its health and preventing skin cancer. Incorporating sunscreen with a broad-spectrum SPF and following sun-safe practices are essential steps in safeguarding our skin from the damaging effects of UV radiation. By taking proactive measures, we can enjoy the outdoors while minimizing the risk of skin damage and maintaining a radiant and healthy complexion.
| Tips for Using Sunscreen: | |
| 1. Apply generously: | Ensure all exposed areas of the body are adequately covered with sunscreen. |
| 2. Don't forget sensitive areas: | Pay attention to often overlooked areas such as the ears, back of the neck, and tops of the feet. |
| 3. Check expiration dates: | Expired sunscreen may not provide the level of protection indicated, so be sure to check the expiration date before use. |
| 4. Consider water-resistant formulas: | When engaging in water activities or sweating, opt for water-resistant sunscreen to maintain its effectiveness. |
| 5. Stay hydrated: | Drinking plenty of water helps keep the skin hydrated, reducing the risk of dryness and sun-induced damage. |
FAQ
What are the main causes of skin cancer?
The main causes of skin cancer include exposure to UV rays from the sun or tanning beds, a family history of skin cancer, having fair skin, and a weakened immune system.
What are the common symptoms of skin cancer?
The common symptoms of skin cancer include a change in the appearance of a mole or spot on the skin, such as asymmetry, border irregularity, color variation, diameter larger than a pencil eraser, or evolving shape, size, or color.
How can I prevent skin cancer?
To prevent skin cancer, you should limit your exposure to UV rays by seeking shade, wearing protective clothing, using sunscreen with a high SPF, avoiding tanning beds, performing regular skin self-exams, and visiting a dermatologist for routine check-ups.
Is skin cancer only caused by sun exposure?
No, while excessive sun exposure is a common cause of skin cancer, it can also be caused by other factors such as genetic predisposition, exposure to certain chemicals or radiation, and a weakened immune system.
Are there any effective treatments for skin cancer?
Yes, there are several effective treatments for skin cancer depending on the type, stage, and location. These treatments may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapy.



