Embark on an extraordinary expedition into the captivating world of envisaging the versatile wonders of the sacred grain, maize, transformed into a powdery substance known as corn flour. Discover the enthralling journey of imagination and culinary exploration as we delve into the enchanting allure of this integral ingredient.
Prepare to be spellbound by the kaleidoscope of possibilities that unfold before you as you join us on this gastronomic odyssey. Without the confines of conventional boundaries, allow your senses to traverse through a labyrinth of tantalizing aromas, velvety textures, and harmonious flavors that are synonymous with this extraordinary ingredient.
As we embark on this evocative expedition, envision yourself being embraced by an ethereal concoction woven with traditions, history, and innovation. Unleash your inner epicurean explorer and witness the symbiosis of cultures as they converge and manifest in the symphony of flavors provided by this humble yet paramount grain.
The Origins and History of Corn Flour
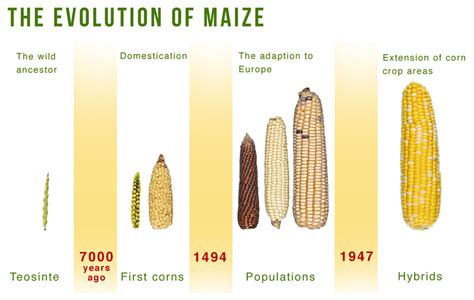
In this section, we will explore the intriguing origins and rich history of corn flour. This essential ingredient has been a staple in various cultures throughout centuries, playing a crucial role in shaping culinary traditions and food production.
Corn flour, also known as maize flour, has a diverse cultural heritage that spans across continents. Its story begins in the Americas, where corn cultivation originated thousands of years ago. Native American civilizations such as the Maya, Aztec, and Inca recognized the value of maize and developed advanced farming techniques to cultivate this versatile crop.
The usage of corn flour quickly spread beyond the Americas, reaching Europe during the age of exploration. Explorers and traders introduced maize to the Old World, where it gained popularity as both a nutritious food source and a valuable trading commodity. The cultivation of maize flour then expanded to Africa, Asia, and other parts of the world, becoming a vital element in the diets of diverse communities.
Throughout history, corn flour has played a significant role in traditional cuisines worldwide. It has been used to create a wide array of dishes, from tortillas and tamales in Mexico to arepas in Colombia, polenta in Italy, and makkai ki roti in India. The versatility and nutritional benefits of corn flour have made it a beloved and essential ingredient in many culinary traditions.
Moreover, corn flour has been a driving force in agricultural and industrial advancements. The development of specialized milling techniques, such as stone grinding and industrial milling, has made the production of corn flour more efficient and accessible. This has allowed for the mass production of various corn-based products, contributing to the global food supply and economic growth.
Today, corn flour continues to be a cherished ingredient and an integral part of global food culture. Its rich history and cultural significance remind us of the enduring impact and importance of maize flour in our everyday lives.
| Advancements | Cultivation Techniques | Culinary Traditions |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial milling | Native American farming methods | Tortillas, tamales, arepas, polenta, makkai ki roti |
| Stone grinding | European introduction of maize | |
| Spread to Africa, Asia, and beyond |
Discover the Health Benefits of Cornmeal
Exploring the numerous advantages of incorporating cornmeal into your diet can be an enlightening experience. This article aims to shed light on the various health benefits associated with this versatile and nutrient-packed ingredient.
Table 1 below provides an overview of the essential nutrients found in cornmeal, highlighting their respective functions and contributions to overall well-being:
| Nutrient | Function | Contribution |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber | Promotes digestion and aids in weight management | Keeps the digestive system healthy and lowers the risk of certain diseases |
| Protein | Essential for growth, repair, and maintenance of cells and tissues | Supports muscle development, strengthens the immune system, and provides energy |
| Vitamins | Play a crucial role in various bodily functions | Contribute to the maintenance of good vision, strong bones, a healthy nervous system, and overall vitality |
| Minerals | Essential for proper body functions and metabolic processes | Support the formation of strong bones, teeth, and red blood cells, and aid in nerve function and enzyme production |
| Antioxidants | Protect the body against free radicals and oxidative stress | May help reduce the risk of chronic diseases, including heart disease and certain types of cancers |
In addition to the rich nutrient content mentioned above, incorporating maize flour into your diet may offer additional health benefits:
- May assist in maintaining healthy cholesterol levels.
- Can aid in stabilizing blood sugar levels, which is especially beneficial for individuals with diabetes.
- May help promote satiety and aid in weight management due to its high fiber content.
- Could potentially enhance digestive health and alleviate constipation.
- May contribute to eye health due to its content of carotenoids and zeaxanthin.
- Could potentially boost immune system function due to the presence of essential vitamins and minerals.
It is important to note that while maize flour offers various health benefits, moderation and a well-balanced diet are key factors in deriving optimal nourishment for overall health and well-being.
Culinary Uses and Recipes: Unleashing the Versatility of Maize Flour

Embark on a gastronomic adventure as we explore the myriad culinary applications and tantalizing recipes that can be created using the exquisite maize flour. Discover the diverse options that maize flour offers to elevate your cooking endeavors and satisfy your taste buds.
1. Traditional Delights
Maize flour, with its rich heritage, holds a special place in traditional cuisines around the world. From soul-warming tortillas and crispy cornbread to delicate arepas and comforting polenta, maize flour provides the foundation for iconic dishes that have stood the test of time.
2. Global Fusion
Embrace the versatility of maize flour and embark on a journey of fusion cuisine. Experiment with incorporating maize flour into non-traditional recipes to create unique flavor profiles. Whether it's adding a hint of maize flour to the batter of fluffy pancakes or creating a delectable maize flour crust for an unconventional pizza, the possibilities are endless.
3. Gluten-Free Goodness
For those with gluten sensitivities or dietary restrictions, maize flour is a valuable alternative. With its naturally gluten-free composition, it serves as a reliable ingredient in creating delicious gluten-free treats. Indulge in mouthwatering cornbread, tender cakes, and scrumptious cookies, all made possible by the remarkable maize flour.
4. Culinary Innovations
Unleash your creativity and explore the uncharted territories of maize flour in culinary experimentation. Enrich your sauces with maize flour as a thickening agent or use it as a binder in savory fritters and vegetarian patties. The distinctive texture and flavor of maize flour will undoubtedly add a delightful twist to your culinary creations.
5. Unexpected Sweetness
Step into the realm of sweet indulgence with maize flour as your guide. Discover the delightful combination of maize flour and natural sweeteners to craft remarkable desserts. From luscious cornmeal cookies to decadent maize flour cakes, let the unique taste of maize flour infuse your desserts with a touch of remarkable sweetness.
Whether you embrace the traditional classics, experiment with fusion cuisine, cater to special dietary needs, embrace culinary innovations, or explore unexpected sweet flavors, maize flour opens up a world of culinary possibilities. Let your imagination run wild as you explore the endless potential of this remarkable ingredient.
Discovering Various Varieties of Corn Flour
In this section, we will embark on a journey of exploring the diverse range of corn flour available in the culinary world. We will delve into the distinctive characteristics and uses of different types of corn flour, offering a comprehensive understanding of this essential ingredient.
Maize Flour in Traditional and Indigenous Cuisines

Exploring the culinary traditions of various cultures, one cannot overlook the significance of maize flour. This staple ingredient has played a vital role in the food culture of many indigenous communities, offering a versatile foundation for countless traditional dishes.
Across the world, regional cuisines have evolved unique ways of incorporating maize flour into their recipes. From tortillas in Mexico to polenta in Italy, maize flour has been a beloved ingredient, cherished for its distinct taste and nutritional value.
Indigenous communities have long recognized the exceptional qualities of maize flour. It has not only served as a primary source of sustenance but has also held cultural significance, often celebrated in rituals and festivals. The preparation and use of maize flour have been passed down through generations, preserving culinary traditions and connecting individuals to their heritage.
One of the notable characteristics of maize flour is its ability to adapt to different cooking methods and flavor profiles. It can be transformed into a thick porridge, used as a batter for frying, or as a binding agent for various dishes. Its versatility allows for a diverse range of delicacies, each showcasing the unique cultural identity of the community it originates from.
- In Mexican cuisine, maize flour is a key component in the preparation of tortillas, tamales, and enchiladas. The fine texture and distinct flavor of maize flour contribute to the authenticity of these traditional dishes.
- In African cuisine, maize flour is commonly used to make dishes such as sadza, a stiff porridge-like staple in many Southern African countries. This hearty dish is often enjoyed with stews, meats, or vegetables.
- In Italian cuisine, maize flour is transformed into polenta, a creamy and satisfying dish that can be cooked to different consistencies and served alongside various accompaniments such as meat, fish, or vegetables.
As societies become more interconnected, the appreciation for traditional and indigenous cuisines has grown. Maize flour, with its rich history and culinary significance, continues to inspire curiosity and exploration of diverse cultures around the world.
The Journey of Maize Flour: From Kernel to Powder
Discover the intricate process involved in transforming maize kernels into the versatile and widely used maize flour. This section will take you through each step, showcasing the methods and techniques employed to produce this essential ingredient.
Step 1: Harvesting and Drying
The journey of maize flour starts with the careful harvesting of mature maize cobs. Once harvested, the cobs are meticulously dried to reduce moisture content, ensuring optimal storage and preventing mold formation.
Step 2: Dehusking and Cleaning
After drying the maize cobs, the next step involves removing the outer husks. This process can be accomplished manually or using mechanized dehusking machines. The dehusked maize is then thoroughly cleaned to eliminate any impurities or foreign matter.
Step 3: Milling
With the dehusked and cleaned maize grains ready, they undergo milling, where they are crushed and ground into a fine powder. This is achieved through the utilization of various mill types, such as hammer mills or roller mills.
Step 4: Sifting and Packaging
The milled maize flour is carefully sifted to remove any remaining impurities or coarse particles, resulting in a smooth and refined texture. Finally, the flour is packaged in suitable containers, ready to be distributed and used in various culinary creations.
Step 5: Nutritional Value
Aside from its culinary applications, maize flour is also highly valued for its nutritional content. Rich in essential vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber, it provides a vital energy source and contributes to a balanced diet.
Understanding the process behind making maize flour allows us to appreciate the dedication and craftsmanship involved in ensuring its quality and versatility. From the cultivation of maize to the milling process, each step is essential in producing this staple ingredient that has become a fundamental part of numerous cuisines around the world.
Impact of Maize Flour Production on the Environment
In this section, we will explore the various ways in which the production of maize flour affects the environment. We will delve into the ecological consequences of maize cultivation, the impact of pesticides and fertilizers used in maize production, and the role of deforestation in maize farming.
Maize cultivation, synonymously known as corn farming, has significant implications for the environment. This staple crop requires vast amounts of water, land, and resources to sustain its growth. The intensive use of water and land in maize production can lead to soil erosion, water pollution, and depletion of natural resources.
- Soil erosion: The extensive cultivation of maize can result in soil erosion due to the removal of natural vegetation cover. Without the protective layer of plants, soil is more susceptible to erosion from wind and water, leading to decreased soil fertility and loss of valuable nutrient-rich topsoil.
- Water pollution: The use of pesticides and chemical fertilizers in maize farming can contaminate nearby water sources. These harmful substances can leach into rivers, streams, and groundwater, posing a threat to aquatic ecosystems and potentially compromising the quality of drinking water.
- Resource depletion: Maize production relies heavily on the use of fertilizers, which often contain nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus. Excessive fertilization can lead to nutrient runoff, where these compounds enter water bodies and cause eutrophication. This process degrades water quality and negatively impacts aquatic life.
In addition to these ecological consequences, the production of maize flour contributes to deforestation. As demand for maize increases, farmers may clear forests to make way for larger fields or expand existing ones. This deforestation disrupts natural ecosystems, contributes to climate change, and reduces biodiversity.
Understanding the environmental impact of maize flour production is crucial for developing sustainable agricultural practices and mitigating the adverse effects on our planet. By exploring alternative farming methods, implementing efficient irrigation systems, and minimizing the use of pesticides and fertilizers, we can strive towards more environmentally-friendly maize production.
Maize Flour in Global Agriculture and Economy
Maize flour, a widely consumed commodity in various regions around the world, plays a crucial role in global agriculture and economy. This versatile product derived from maize grains, also known as corn, serves as a staple food for many countries and contributes significantly to their agricultural and economic development.
Maize flour production and consumption have a significant impact on the agricultural sector. The cultivation of maize crops not only provides employment opportunities for farmers but also contributes to the overall growth of the agricultural industry. The high demand for maize flour stimulates farmers to expand their production capacities, leading to increased agricultural productivity and income generation.
Furthermore, the global economy greatly relies on maize flour as it serves as a key ingredient in a wide range of food products. From bread and tortillas to breakfast cereals and snacks, maize flour is a crucial component that adds nutritional value, texture, and taste to these food items. Its widespread use in the food industry creates a demand that drives economic activities and trade, benefiting both producers and consumers.
- Maize flour as a staple food in various cultures
- Maize flour's contribution to food security
- Maize flour in the international trade market
- Maize flour's impact on employment and income generation
- Maize flour as a key ingredient in the food industry
- Maize flour's nutritional value and health benefits
- Maize flour production and technology advancements
In conclusion, maize flour plays a vital role in global agriculture and economy. Its production, consumption, and utilization in various food products have significant economic and social implications. Understanding the importance of maize flour in both local and international contexts is essential for promoting sustainable agricultural practices and ensuring food security for future generations.
The Future of Cornmeal in Food Innovation

In this section, we will explore the potential advancements and exciting prospects that lie ahead for cornmeal in the world of food innovation. As the culinary landscape continually evolves, cornmeal, a versatile and nutritious ingredient, is poised to play a significant role in shaping the future of food.
1. Diversifying Culinary Applications: As food trends embrace diversity and exploration, cornmeal has the potential to bring a new dimension to various culinary applications. Its unique texture and flavor can be incorporated into a wide range of dishes, from traditional recipes to innovative creations, adding depth and complexity to the dining experience. |
2. Health Benefits: Beyond its culinary versatility, cornmeal offers notable health benefits as well. It is a rich source of essential nutrients, including dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals. As health-conscious consumers seek nutritious and wholesome options, cornmeal can serve as a valuable component in creating balanced and nourishing meals. |
3. Sustainable Agriculture: In an era marked by increasing concerns about sustainability and environmental impact, cornmeal presents an opportunity to promote sustainable agriculture practices. As the world looks for alternatives to traditional grain crops, cornmeal, with its high yield and adaptability, can contribute to a more sustainable and resilient food system. |
4. Culinary Innovation: As chefs and food scientists continue to push boundaries in culinary innovation, cornmeal can serve as a canvas for creative experimentation. From textured coatings to gluten-free baking, cornmeal's diverse applications offer endless possibilities for exploring new taste profiles and expanding the boundaries of gastronomy. |
In conclusion, the future of cornmeal in food innovation is bright and promising. Its versatility, health benefits, sustainability, and ability to inspire culinary creativity position it as a vital ingredient in shaping the future of food. Embracing the potential of cornmeal opens up exciting opportunities for both chefs and consumers, leading to a more diverse, nutritious, and sustainable culinary landscape.
FAQ
What is maize flour?
Maize flour, also known as corn flour, is a fine powder made by grinding dried corn kernels. It is a staple food in many countries, especially in regions where corn cultivation is prevalent.
How is maize flour made?
Maize flour is made by drying corn kernels and then grinding them into a fine powder. The dried kernels are first soaked in water, and then they are ground using a grinding stone, mill, or machine. The resulting powder is maize flour.
What are the uses of maize flour?
Maize flour has numerous uses in cooking and baking. It is commonly used as a thickening agent in soups, gravies, and sauces. It is also used in making various types of bread, tortillas, and pancakes. Additionally, maize flour can be used in desserts and as a coating for fried foods.
Is maize flour gluten-free?
Yes, maize flour is gluten-free. It does not contain the protein gluten, which is found in wheat, barley, and rye. Therefore, maize flour is a suitable alternative for individuals with gluten intolerance or those following a gluten-free diet.
What are the nutritional benefits of maize flour?
Maize flour is rich in carbohydrates, dietary fiber, and various vitamins and minerals. It is a good source of energy and provides essential nutrients like vitamin B6, magnesium, and potassium. However, it is important to note that the nutritional profile may vary depending on the quality and processing of the maize flour.
What is maize flour?
Maize flour is a type of flour that is made from grinding dried corn kernels. It is commonly used in various cuisines around the world and is a staple ingredient in many traditional dishes.
What are the health benefits of consuming maize flour?
Consuming maize flour can provide several health benefits. It is a good source of dietary fiber, which helps in digestion and keeps you feeling full for longer. It also contains essential vitamins and minerals like iron, magnesium, and phosphorus. Additionally, maize flour is gluten-free, making it suitable for individuals with gluten intolerance or celiac disease.



