In the realm of gardening, there exists a fascinating realm of soil that has long tantalized the senses of enthusiasts and green thumbs alike. This mystical landscape, with its rich and organic texture, carries a certain allure that draws in the most intrepid gardeners. It invites exploration, offering a world of untapped potential and untold benefits. Broaching the subject of this seductive earth, we delve into the realm of clay soil, a realm that, despite its challenges, offers a myriad of rewards for those willing to embrace its complexities and harness its hidden powers.
For the ambitious gardener, clay soil presents a unique set of opportunities. Its dense structure provides a sturdy foundation for plants, granting them stability and support as they grow. This robust quality allows for vertical gardening and offers a canvas for creating breathtaking landscapes that showcase the beauty of cascading vines and multilayered floral sculptures. Additionally, clay soil possesses exceptional water retention qualities, ensuring that plants receive a steady supply of moisture amidst dry spells or periods of limited rainfall.
However, beneath the surface of this captivating clay earth lies a web of challenges waiting to be overcome. The compact nature of clay soil presents difficulties with regards to proper drainage, as water tends to accumulate and saturate the soil. The density also results in reduced oxygen flow, making it harder for plant roots to breathe and absorb vital nutrients. Moreover, clay soil's tendency to harden when dry and form stubborn clods can thwart the gardening efforts of even the most dedicated horticulturists. But fear not, for with careful planning, strategic planting, and informed techniques, these obstacles can be overcome, opening the door to the full potential of clay soil gardening.
Deciphering the Nature of Clay Soil: Resolving its Composition and Distinctive Attributes
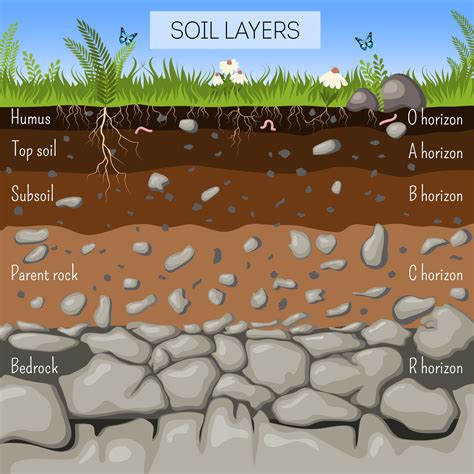
In this section, we will delve into the intricacies surrounding clay soil, exploring its fundamental composition and unique characteristics. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the nature of clay soil, you will be better equipped to comprehend its impact on gardening and explore effective strategies for cultivation.
To appreciate the essence of clay soil, it is imperative to comprehend its composition. This type of soil is predominantly composed of tiny mineral particles that are densely packed together. Due to its cohesive nature, clay soil exhibits a distinct ability to retain water and nutrients, bringing both advantages and challenges to gardening endeavors. Furthermore, the compact structure of clay soil grants it an exceptional capacity to retain moisture, making it particularly predisposed to waterlogging and subsequent drainage issues.
Furthermore, it is crucial to recognize the unique characteristics inherently associated with clay soil. Its high plasticity grants it the capability to be molded, making it ideal for pottery and sculpting. However, in the context of gardening, this plasticity can pose challenges. The tight structure of clay soil hampers proper root development and leads to poor aeration, impeding optimal plant growth and reducing overall productivity.
- Retention of Nutrients: Clay soil's ability to hold onto nutrients can be advantageous, ensuring plants have a steady supply for growth.
- Slow Drainage: Excessive water retention in clay soil can result in poor drainage, which may suffocate plant roots and encourage the growth of water-loving fungi.
- Potential for Compaction: The compact nature of clay soil makes it prone to compaction, reducing pore space and hindering root penetration. Regular soil amendments are necessary to alleviate this issue.
Understanding the composition and characteristics of clay soil lays the groundwork for effectively managing its challenges and harnessing its benefits. By implementing appropriate cultivation techniques and incorporating organic matter, it is possible to improve drainage, enhance structure, and make clay soil more suitable for successful gardening endeavors.
The Advantages of Clay Soil for Cultivating Plants
In the world of gardening, the type of soil one has plays a crucial role in determining the success and vibrancy of the plants grown. Clay soil, often overlooked and underestimated, holds a range of benefits that make it an excellent choice for cultivators.
1. Nutrient Retention: Clay soil exhibits exceptional nutrient retention properties, supplying plants with a reserve of necessary minerals and elements they need to thrive. The compact nature of clay particles can prevent leaching, ensuring that valuable nutrients are not washed away by rainwater or irrigation.
2. Moisture Holding: One of the standout features of clay soil is its ability to hold moisture for extended periods. The dense composition of clay particles helps to retain water, making it an ideal choice for plants that require consistent soil moisture. This characteristic can be especially advantageous in arid or drought-prone regions, where water conservation is essential.
3. Soil Fertility: Clay soil often contains a rich abundance of organic matter. This organic matter enhances the fertility of the soil, providing a favorable environment for microorganisms and earthworms that contribute to the overall health of the soil ecosystem. Additionally, the high cation exchange capacity of clay soil facilitates nutrient availability to plants.
4. Soil Structure: Clay soil possesses superb structural stability, creating a solid foundation for plant roots to anchor and grow. The cohesive nature of clay particles prevents soil erosion and promotes strong root development, resulting in healthier and more robust plants. Moreover, the fine texture of clay soil allows for optimum air circulation, promoting root respiration.
5. Versatility: Despite its reputation for being challenging to work with, clay soil can be successfully managed and utilized in various ways. When properly amended with organic matter and subjected to appropriate cultivation techniques, clay soil can become an incredibly productive medium for growing a wide range of plants, including vegetables, flowers, and ornamentals.
When contemplating a gardening endeavor, clay soil should not be overlooked. Its beneficial characteristics provide a solid foundation for plants to flourish, making it an invaluable asset to any gardener.
The Obstacles of Cultivating in Clay-like Terrain

Exploring the intricacies of working with a soil composition resembling clay poses a plethora of challenges and considerations for garden enthusiasts. The properties of this dense and compact earth can significantly impact the growth and overall health of plants and vegetation.
One of the key challenges of gardening in clay-like soil is its poor drainage capabilities. Due to its dense nature, excess moisture tends to accumulate within the soil, leading to waterlogged conditions that can hinder root development and contribute to root rot. Additionally, clay soil has a tendency to become compacted, making it harder for plants to establish their root systems and access necessary nutrients.
Moreover, clay soil can limit a gardener's options when it comes to plant selection. Not all plants can thrive in such soil conditions, as they require adequate aeration and drainage to grow optimally. Careful consideration and research are essential to identify plant varieties that are resilient and adaptable to the challenges that clay soil presents.
When it comes to cultivation techniques, amending clay soil becomes crucial to improve its structure and drainage abilities. The addition of organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, can help break up the dense composition and increase its permeability. Regular soil testing is also advisable to monitor nutrient levels and adjust fertilization accordingly, ensuring plants receive the essential elements they require.
| 1. | Amend soil with organic matter regularly. |
| 2. | Practice crop rotation to maintain soil health. |
| 3. | Utilize raised beds or containers for better drainage. |
| 4. | Water deeply but infrequently to avoid waterlogging. |
| 5. | Consider planting native vegetation known to thrive in clay soil. |
Though challenges may abound, successfully cultivating in clay-like soil is indeed attainable with the right techniques and plant choices. By understanding the drawbacks and implementing strategies to overcome them, gardeners can create thriving green spaces even in the face of such adversity.
Enhancing Clay Soil: Approaches and Additives
In this section, we will explore various methods and substances that can be used to enhance the quality of clay soil, allowing it to become more conducive to successful gardening endeavors. By implementing these techniques and utilizing appropriate amendments, gardeners can transform their clay soil into a fertile and productive medium for plants to thrive.
1. Loosening the Soil Structure
To counteract the compactness of clay soil, it is essential to implement strategies that promote better aeration and drainage. One effective technique is to incorporate organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure into the soil. This loosens the structure and helps create air pockets, allowing roots to penetrate easily and water to drain more efficiently.
Additionally, performing regular deep cultivation with suitable garden tools can break up compacted clay particles and improve overall soil structure, providing space for roots to grow more freely. Care should be taken not to overwork the soil, as excessive tilling may result in the breakdown of beneficial soil aggregates.
2. Enhancing Nutrient Content
Clay soil tends to retain nutrients more effectively than other soil types, but it may also present challenges in terms of nutrient availability. Adding organic amendments, such as compost, well-decomposed leaves, or aged manure, can help enrich the soil with essential nutrients and promote a balanced nutrient profile.
Furthermore, incorporating slow-release fertilizers into the clay soil can ensure a steady supply of nutrients over an extended period. This approach avoids the risk of nutrient leaching and helps plants maintain optimal growth and development.
3. Improving Drainage
One of the main challenges of clay soils is their poor drainage capacity, leading to waterlogged conditions that can hinder root growth and promote disease. To address this issue, adding materials like perlite, coarse sand, or vermiculite to the soil can improve drainage and prevent excessive water retention.
It is advisable to create raised beds or mounds in areas with heavy clay soil, as this allows for better water runoff and reduces the risk of waterlogged roots. Installing drainage systems, such as French drains or underground pipes, can also help channel excess water away from garden beds.
4. Protective Mulching
Applying a layer of organic mulch, such as straw, wood chips, or shredded leaves, can provide several benefits for clay soil. Mulching helps regulate soil temperature, prevent moisture loss, and suppress weed growth. It also gradually breaks down over time, enriching the soil with organic matter and improving its structure.
In conclusion, amending clay soil requires a multifaceted approach that involves loosening its structure, enhancing nutrient content, improving drainage, and implementing protective mulching. By employing these techniques, gardeners can transform their clay soil into a productive and thriving environment for plants to flourish.
Choose the Perfect Flora for Clay Soil

When cultivating a garden, it is crucial to consider the compatibility between the soil composition and the plants that will flourish in it. Clay soil, known for its rich nutrient content, can be a challenging growing medium but can also provide unique advantages for certain plant varieties. By selecting the right flora for clay soil, gardeners can ensure a successful and thriving garden.
1. Hardy Perennials
Choose plants that have adapted to the dense nature of clay soil, such as hardy perennials. These resilient plants have robust root systems that can penetrate the compacted clay, providing stability and vigor to the garden bed. Examples of hardy perennials suitable for clay soil include asters, coneflowers, daylilies, and sedums.
2. Native Species
Consider incorporating native plant species into your garden design. Native plants have evolved to thrive in the specific soil and climate conditions of the local area. They have adapted over time to clay soil and will typically require less maintenance and resources, while offering a vibrant and sustainable garden. Check with local nurseries or gardening experts for suggestions on the best native plant options.
3. Ornamental Grasses
Adding ornamental grasses to your clay soil garden can bring a touch of elegance and movement. These plants feature fibrous root systems that can break through heavy clay, allowing them to establish and flourish. Some attractive options for clay soil include feather reed grass, switchgrass, maiden grass, and fountain grass.
4. Moisture-Loving Shrubs
Select moisture-loving shrubs that can tolerate clay soil conditions. These plants possess adaptability to withstand periods of drought as well as wet soil, which are common characteristics of clay soil. Examples of shrubs that thrive in clay soil include blueberry bushes, hydrangeas, and certain species of viburnum.
5. Soil Amendments
Make use of organic soil amendments to improve the structure and drainage of clay soil. Incorporating well-rotted compost, aged manure, and gypsum can help break up the heaviness of the clay, enhancing its fertility and reducing compaction. These amendments will create a more suitable environment for a wider variety of plants.
By carefully selecting flora that is compatible with clay soil, gardeners can overcome the challenges and maximize the benefits of this unique growing medium. With the right plants and proper soil amendments, a clay soil garden can become a lush and thriving oasis.
Techniques for Proper Irrigation with Dense Soil
In this section, we will explore effective methods for watering gardens that are established in clay soil. Understanding the unique properties of clay soil is crucial for maintaining optimal moisture levels and promoting healthy plant growth. By implementing the right watering strategies, gardeners can overcome the challenges presented by clay soil and create thriving gardens.
1. Deep and Infrequent Watering
When watering clay soil, it is important to provide a thorough soak to ensure the water penetrates deep into the soil. This encourages the plants' roots to grow deeper, enhancing their ability to access nutrients and moisture. It is recommended to water less frequently but for longer durations, allowing the water to reach the lower layers of the soil.
2. Mulching for Moisture Retention
Applying a layer of organic mulch, such as straw or wood chips, around your plants can help retain moisture in clay soil. Mulching helps prevent evaporation and slows down the water runoff, allowing the soil to absorb the moisture more effectively. Additionally, the mulch acts as insulation, protecting the plants' root systems during extreme temperatures.
3. Watering Early in the Day
Watering your garden in the early morning is ideal for clay soil. This timing allows the water to penetrate the soil before the heat of the day causes excessive evaporation. Watering in the evening may lead to prolonged soil moisture, increasing the risk of diseases and pests. Additionally, watering early in the day gives the plants enough time to dry, reducing the likelihood of fungal growth.
4. Monitoring Soil Moisture Levels
Regularly monitoring the moisture levels in clay soil is essential to avoid both over and under-watering. Use a moisture meter or simply dig a small hole in the soil to assess its moisture content. Adjust your watering schedule accordingly to maintain a consistent level of moisture in the soil, ensuring optimal growing conditions for your plants.
5. Implementing Drip Irrigation Systems
Installing a drip irrigation system can be highly beneficial for gardens with clay soil. Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the base of the plants, minimizing water wastage and allowing for more efficient watering. The slow and steady flow of water prevents surface runoff and enhances optimal moisture distribution in clay soil.
By applying these watering strategies and techniques, gardeners can successfully navigate the challenges associated with clay soil and create beautiful and thriving gardens.
Protecting Clay Soil from Erosion

Preserving the integrity of clay-rich soil against erosion poses a significant concern for gardeners. This section delves into crucial strategies and practices to safeguard your clay soil from erosion, protecting its fertility and promoting healthy plant growth without compromising its composition.
1. Implementing Mulching Techniques
One effective method to prevent erosion is through the use of mulch. Applying a layer of organic matter, such as straw, leaves, or wood chips, helps to retain moisture, regulate soil temperature, and reduce water runoff. Mulching also adds organic nutrients to the clay soil, enhancing its structure and fertility.
2. Creating Terraces and Contour Planting
Dividing the landscape into terraces and planting contour crops can effectively mitigate erosion. By implementing terraces along slopes, water runoff is significantly reduced, allowing it to soak into the soil gradually. Contour planting involves arranging plants, shrubs, or trees in a wave-like pattern, helping to break the flow of water and prevent soil erosion.
3. Installing Retaining Walls
For areas with steep slopes, the installation of retaining walls can be beneficial in preventing erosion. These walls, constructed using sturdy materials like stone or concrete, help to hold back the soil and prevent it from being washed away during heavy rainfall or storms. This ensures the stability of the clay soil and protects against erosion.
4. Applying Terraseeding Techniques
Terraseeding involves planting grass seeds or other erosion-resistant ground covers on terraced slopes. This technique aids in stabilizing the soil, reducing rainfall impact, and preventing erosion. It also provides additional vegetation to enhance the aesthetic appeal of the garden while protecting the clay soil.
5. Creating Water Diversion Systems
Constructing adequate water diversion systems, such as swales or channels, helps to redirect excess water away from vulnerable areas of clay soil. These systems effectively guide water to suitable drainage paths, minimizing the risk of erosion and waterlogged conditions that can negatively impact plant growth.
By employing these strategies and techniques, you can effectively protect your clay soil from erosion, ensuring its longevity and fertility while creating an optimal gardening environment.
Gardening Suggestions for Achieving Success with Clay Soil
Discover the secrets to blooming gardens and thriving plants amidst the unique challenges of clay soil. By implementing these expert tips, you can turn the potential difficulties of cultivating in clay soil into opportunities for growth and abundance.
Select Hardy Plant Varieties: When gardening in clay soil, choose plants that have a natural resilience and adaptability to withstand the soil's unique texture and composition. Look for species that have deep root systems, as they can better penetrate the compacted clay and access essential nutrients and moisture.
Amend the soil: Improve the overall structure and drainage of clay soil by incorporating organic matter such as compost, well-rotted manure, or leaf mold. These amendments will help break up the compacted particles, increase porosity, and enhance nutrient retention, promoting healthier root development and overall plant growth.
Practice proper watering: Clay soil has a tendency to retain water, which can lead to waterlogged roots and rot. Ensure proper drainage by watering deeply but infrequently, allowing the soil to dry out slightly between watering sessions. Additionally, consider using raised beds or planting on slopes to facilitate better water drainage.
Maintain a thick layer of mulch: Apply a generous layer of organic mulch, such as wood chips or straw, around your plants. This will help regulate soil temperature, suppress weed growth, and reduce water evaporation, all while slowly decomposing and enriching the soil with valuable organic matter.
Implement proper soil cultivation techniques: Avoid excessive tilling or digging in clay soil, as this can worsen compaction and disrupt the soil structure. Instead, gently loosen the top few inches of soil using a garden fork or cultivator. This will promote aeration and improve water infiltration without causing excessive damage to the soil's natural composition.
Monitor soil fertility: Regularly test the nutrient levels in your clay soil to ensure proper fertilization. Use organic fertilizers high in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium to replenish any deficiencies and enhance plant growth. By maintaining adequate soil fertility, you can support the health and vitality of your garden's plants.
With these valuable gardening suggestions, you can overcome the challenges of clay soil and transform your dream of a flourishing garden into a reality. By understanding the unique characteristics of clay soil and implementing the appropriate techniques, you'll be well on your way to gardening success.
FAQ
What are the benefits of clay soil for gardening?
Clay soil has excellent water retention properties, which means plants can better withstand drought conditions. Clay is rich in nutrients and minerals, providing a fertile environment for plant growth. Additionally, clay soil has good structure, which helps roots anchor firmly and prevents erosion.
What are the challenges of gardening in clay soil?
Gardening in clay soil can be challenging due to its heavy and compact nature. It drains poorly, causing waterlogging and root rot. Clay soil also tends to harden when dry, making it difficult for young plants to push through. Its compactness restricts root development and nutrient absorption, leading to stunted growth.
How can I improve clay soil for gardening?
Improving clay soil starts with adding organic matter such as compost, leaf mold, or well-rotted manure. This helps improve drainage, loosens compacted soil, and enhances its fertility. It is advisable to avoid excessive tilling or digging when the soil is wet to prevent compaction. Amending with sand or gypsum can also aid in breaking up clay particles.
What are some tips for successful gardening in clay soil?
When gardening in clay soil, it is essential to choose plant varieties that tolerate or thrive in such conditions. Raised beds or container gardening can provide better drainage and prevent waterlogging. Regularly adding organic matter, using mulch, and applying appropriate watering techniques can help maintain soil moisture levels and improve the overall health of plants.
Can clay soil be converted into loam or sandy soil?
Clay soil can be improved over time, but converting it into loam or sandy soil might be challenging. Sandy soil can be added to increase drainage, and organic matter can be incorporated to improve texture. However, complete transformation into loamy or sandy soil may not be achievable, as clay particles are a fundamental aspect of the soil composition.
What are the benefits of clay soil for gardening?
Clay soil has several benefits for gardening. It retains nutrients and moisture well, making it suitable for plants that prefer a moist environment. Clay soil also has good fertility, which can support the growth of healthy plants. Additionally, clay soil has excellent water-holding capacity, reducing the need for frequent watering.
What are the challenges of gardening in clay soil?
Gardening in clay soil comes with a few challenges. One of the main difficulties is the soil's poor drainage, which can lead to waterlogged conditions and root rot. Clay soil also tends to compact easily, making it harder for plant roots to establish and grow. Additionally, clay soil can become heavy and sticky when wet, making it difficult to work with and causing it to become hard and crack when dry.



