Prepare to embark on a captivating journey through the enigmatic and captivating shadows of a world shrouded in darkness. In this realm of mystery and intrigue, where the absence of light reigns supreme, we invite you to explore the depths of a substance that holds an inherent allure - the alluring black coal, or as some may call it, the mesmerizing obsidian.
By delving into the secrets of this pitch-black entity, we endeavor to unravel the hidden wonders that lie within its depths. Its ebony hue and enigmatic properties have fuelled the imaginations of countless generations, sparking both reverence and curiosity. As we navigate through the labyrinthine underworld of black coal, tantalizing secrets await us at every turn.
Prepare to witness the surreal beauty that hides within the ebony bosom of this mysterious material. Its glossy surface, seemingly void of life, conceals a rich history carved by time itself. The ancient tales whispered by this enigmatic substance speak of struggles, transformations, and the very essence of life's energy forged within its core.
Take a moment to envision a world devoid of light, where the shadows hold the secrets of creation. As we venture into this realm of darkness, we discover that black coal is far more than a mere rock; it is a portal to the past and a key to the future. Its significance stretches beyond its practical uses, as it embodies the power of perseverance, metamorphosis, and unyielding strength.
The Fascinating History of Coal Mining
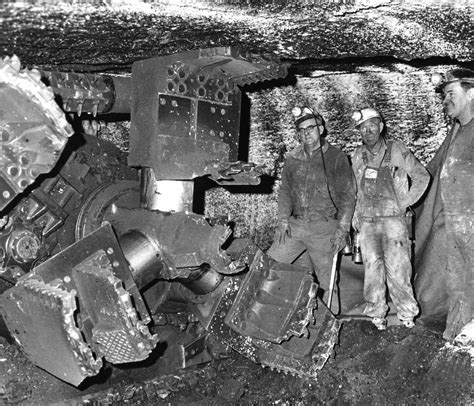

In this section, we will delve into the captivating past of coal mining, exploring its significance and impact on various aspects of human civilization. From its humble beginnings to its pivotal role in driving industrialization, the history of coal mining is a tale of perseverance, progress, and profound influence.
1. Origins and Early Techniques
- Early discoveries and utilization of coal deposits
- The primitive methods employed for extraction
- The gradual improvements and innovations in mining techniques
2. Coal Mining in Ancient Civilizations
- The integral role of coal in ancient societies
- The ancient mining practices adopted by civilizations such as the Romans and Chinese
- The cultural, economic, and social implications of coal mining in these civilizations
3. Coal Mining during the Industrial Revolution
- The transformative impact of coal mining on industrialization
- The emergence of large-scale mining operations
- The technological advancements that revolutionized the coal mining industry
4. Environmental and Social Shifts
- The environmental effects of coal mining
- The evolution of safety measures and labor rights
- The socioeconomic changes brought about by coal mining
5. Modern-Day Coal Mining
- The current state of the coal mining industry
- Contemporary mining techniques and technologies
- The ongoing debates surrounding coal as an energy source
By exploring these historical aspects, we can gain a deeper understanding of the profound impact that coal mining has had on our world. From its roots in antiquity to its modern-day significance, coal mining remains an integral part of our history and continues to shape our present and future.
Coal as a Power Source and Its Environmental Impact
The utilization of coal as a primary energy source has been an integral part of global industrialization for centuries. However, the widespread use of coal has brought about numerous environmental challenges, prompting the need for alternative energy solutions. This section will explore the significance of coal as an energy source and delve into its environmental implications.
1. The Importance of Coal as an Energy Source:
Coal has played a crucial role in transforming societies and powering economies, serving as a reliable source of heat, electricity, and fuel for various industrial processes. Its abundance, cost-effectiveness, and high energy density make it an attractive choice, especially in regions rich in coal deposits. The extensive use of coal has contributed significantly to the growth of sectors such as manufacturing, transportation, and electricity generation.
2. Environmental Impact of Coal Exploitation:
Despite its benefits, coal extraction and combustion have severe detrimental effects on the environment. The mining process involves extensive deforestation, habitat destruction, and soil erosion. Additionally, coal mines often produce toxic wastewater and release harmful gases, including sulfur dioxide and methane, into the atmosphere, contributing to air pollution and climate change. Furthermore, the burning of coal emits large quantities of carbon dioxide, the primary greenhouse gas responsible for global warming.
3. Efforts to Mitigate Environmental Harm:
Recognizing the environmental risks associated with coal, numerous efforts have been made to mitigate its impact. Technologies such as carbon capture and storage (CCS) aim to capture and store CO2 emissions from coal-fired power plants underground. Renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and hydroelectric power are being increasingly utilized as alternatives to coal. Additionally, stringent regulations and policies are being implemented worldwide to enforce cleaner coal technologies and promote sustainable coal mining practices.
4. The Future of Coal and Energy Transition:
As the world shifts towards a more sustainable and low-carbon future, the role of coal is likely to diminish. While coal still dominates energy production in several regions, the importance of transitioning towards renewable energy sources cannot be overstated. Governments and industries worldwide are investing in research and development of cleaner coal technologies and exploring ways to diversify their energy portfolios. This transition will not only reduce environmental impacts but also pave the way for a more resilient and sustainable energy future.
In conclusion, coal has been an indispensable energy source driving socio-economic development, but its exploitation and use have significant environmental consequences. Recognizing these challenges, efforts are underway to mitigate the environmental harm caused by coal and transition towards cleaner and more sustainable energy alternatives. By fostering innovation and embracing energy transition, we can effectively address the environmental impact of coal while ensuring a secure and environmentally conscious energy future.
The Formation Process of Coal: Nature's Ancient Treasure
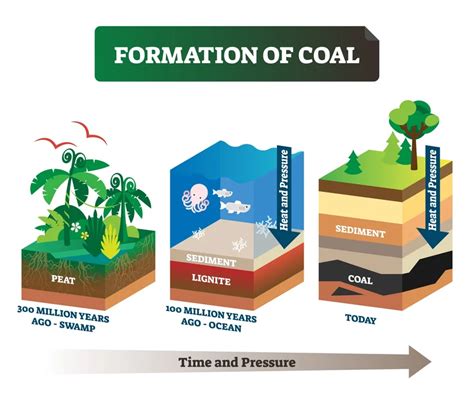
Exploring the intricate journey that transforms organic matter into the remarkable substance known as coal.
Coal, a fascinating and invaluable natural resource, evolves through a complex process spanning millions of years. This extraordinary transformation occurs as the remains of ancient plants, trees, and other organic materials undergo a metamorphosis under the earth's surface. As time passes, heat, pressure, and other geological forces exert their influence, progressively turning the initial organic matter into the rich and diverse substance we call coal.
The formation of coal can be simplified into several distinct stages. It all begins with the accumulation of plant debris in a swampy environment. Over time, layers upon layers of decaying plants and trees accumulate, forming a dense mat of organic matter. This biomass gradually submerges beneath water and mud, effectively isolating it from contact with oxygen – a crucial factor in the process ahead.
As sediments continue to accumulate above, the organic matter experiences immense pressure. This pressure compresses the plant material, expelling water and volatile substances, while simultaneously enhancing the carbon concentration. Over the course of millions of years, this gradual compression transforms the organic matter into a precursor substance called peat.
But the journey doesn't end here. The further burial of the peat layers, combined with the intense heat generated by the Earth's internal processes, contributes to the next stage of coal formation – lignite. Lignite, characterized by its relatively low carbon content and high moisture levels, represents an intermediate phase in the coal formation process.
Continued geological forces and transformation processes result in the subsequent stages of coal formation: sub-bituminous, bituminous, and anthracite. Each of these stages sees an increase in carbon content and a decrease in moisture and impurities. Finally, after millions of years of geological activity, the process culminates in the formation of the highly valuable and energy-rich anthracite coal.
- Plant debris accumulates in a swampy environment.
- Layers of decaying plants form a dense mat of organic matter.
- Biomass submerges beneath water and mud.
- The pressure compacts the organic matter, expelling water and volatile substances.
- Peat, a precursor substance, is formed.
- Peat layers are buried further, and heat facilitates the formation of lignite.
- Lignite represents an intermediate phase in coal formation.
- Transformation processes lead to sub-bituminous, bituminous, and anthracite coal.
The remarkable formation process of coal unveils nature's ancient treasure – a valuable resource that has played a pivotal role in the development of civilizations throughout history.
Unveiling the Varieties of Coal
Delve into the intricate world of coal as we explore its diverse types, each possessing its own unique characteristics and applications. With an array of distinct compositions and properties, coal has become a valuable resource utilized in various industries worldwide.
To gain a comprehensive understanding of the different types of coal, let's delve into their classifications based on factors such as carbon content, moisture levels, and energy density. By examining these distinguishing features, we can comprehend the varying uses and qualities associated with each type.
| Type | Carbon Content | Energy Density | Moisture Content | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anthracite | High | High | Low | Heating, electricity generation |
| Bituminous | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Electricity generation, coke production |
| Sub-bituminous | Low to moderate | Low to moderate | Moderate to high | Electricity generation, industrial processes |
| Lignite | Low | Low | High | Electricity generation, fertilizer production |
Aside from these primary classifications, there exist additional subtypes and variations of coal, further enriching the understanding of its complexity. Exploring these different types of coal enables us to appreciate the role they play in powering economies, providing heat, and contributing to the industrial landscape.
The Versatility of Coal in Various Industries
In today's modern world, the utilization of coal extends far beyond its traditional use as a source of energy. The diverse applications of coal span across various industries, highlighting its versatility and indispensable nature. From manufacturing and construction to pharmaceuticals and technology, coal plays a pivotal role in driving innovation and progress.
Manufacturing: Coal serves as a fundamental component in the production processes of numerous manufacturing industries. Its high carbon content and combustible properties make it an excellent choice for metal smelting and the creation of steel and alloys. Additionally, coal-derived chemicals are used in the production of textiles, fertilizers, and even plastics.
Construction: The construction industry heavily relies on coal for multiple purposes. Coal is an essential ingredient in the production of cement, a fundamental building material. It provides the necessary heat during the cement manufacturing process and contributes to the strength and durability of the final product.
Pharmaceuticals: Coal finds utility in the pharmaceutical industry as well. It serves as a vital ingredient in the production of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and acts as a catalyst in numerous chemical reactions. Moreover, coal-based activated carbon is widely used in medicinal products and medical treatments.
Technology: In the ever-evolving world of technology, coal holds its significance. Coal is utilized in the production of silicones, which are critical components in various electronic devices and solar panels. It also plays a crucial role in the creation of carbon fibers, which find applications in aerospace, automotive, and electronic industries.
In conclusion, the versatility of coal is undeniable, with its indispensable presence in multiple industries. From manufacturing to construction, pharmaceuticals, and technology, coal continues to fuel progress and innovation, enabling the advancement of society in numerous aspects.
The Unraveling of Underground Coal Fires
Delving deep into the enigmatic realm beneath our feet, we dare to explore the veiled secrets of underground coal fires. Embarking on this journey of discovery, we aim to uncover the mysteries that shroud these subterranean phenomena.
Coal: a Symbol of Industrial Revolution and Economic Growth
The emergence and significance of coal cannot be overstated when exploring the history of industrial revolution and economic growth. It stands as a cornerstone of progress, marking a transformative era that revolutionized society and propelled nations towards prosperity.
Coal, often referred to as the "black diamond," exemplifies the essence of the industrial revolution. By harnessing its immense energy potential, mankind unlocked vast possibilities that fueled unprecedented advancements in technology, manufacturing, and transportation. |
Heralding an era of innovation and growth, coal served as the catalyst that powered steam engines, enabling factories to mass-produce goods, and facilitating the expansion of rail networks worldwide. This readily available and abundant resource transformed the global economy, triggering a domino effect of industrialization and paving the way for rapid economic development. |
Moreover, coal not only revolutionized industries but also shaped entire regions. Mining towns emerged, forming interconnected networks of labor, production, and commerce. The extraction and distribution of coal generated jobs, fostered urbanization, and spurred the rise of numerous cities that still bear the imprints of the coal-driven past. |
Additionally, the economic impact of coal extended beyond national boundaries. Countries endowed with rich coal reserves gained a strategic advantage, leveraging their resources to solidify their positions in the global market. Coal became a valuable commodity, driving international trade and contributing to the accumulation of wealth for nations that could harness its potential. |
As societies transitioned into a new era marked by accelerated economic growth, coal played an integral role in shaping the world as we know it today. It symbolizes the transformative power of human ingenuity, resourcefulness, and ambition, forever reminding us of the remarkable milestones achieved during the remarkable era of industrial revolution. |
The Hidden Dangers: Potential Health Risks and Respiratory Conditions Associated with Coal
Exploring the darker side of the coal industry unveils a hidden reality, one that goes beyond the surface aesthetics and deep into the health hazards and respiratory diseases it poses. The black substance known as coal, revered for its energy-producing properties, holds within it a perilous secret that can have profound implications on both human and environmental well-being.
Exposure to coal dust and the release of harmful gases during mining, processing, and combustion processes are among the primary contributors to a range of health issues. From chronic respiratory conditions to life-threatening diseases, the impact of coal on individuals and communities cannot be underestimated.
- Airborne Risks: Inhalation of coal dust particles and the emission of toxic gases, such as sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide, can lead to a range of respiratory ailments. These include asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and even more severe conditions like black lung disease.
- Environmental Fallout: Coal production and consumption not only affect human health but also jeopardize the environment. The release of greenhouse gases and particulate matter contributes to air pollution, global warming, and climate change, further exacerbating the health risks associated with coal.
- Occupational Hazards: Coal miners, who toil tirelessly in hazardous conditions, face the greatest risk. Their prolonged exposure to coal dust and toxic fumes puts them at high risk of developing respiratory diseases, including pneumoconiosis, commonly known as black lung disease.
- Vulnerable Communities: The negative consequences of coal extend beyond the workplace. Communities residing near coal mines or power plants are also vulnerable to the adverse effects of coal. Increased rates of respiratory conditions, cardiovascular problems, and reduced overall health are common concerns for these populations.
In light of these alarming health risks, it becomes evident that a comprehensive understanding of the darker side of coal is crucial. Implementing effective preventive measures, transitioning towards cleaner alternatives, and prioritizing the well-being of both individuals and the planet are essential steps towards a healthier future.
The Future of Coal: Challenges and the Transition to Clean Energy

In this section, we will explore the upcoming challenges and the gradual shift towards clean energy in relation to coal. Moving away from its enigmatic and dark reputation, the future of coal is at a crossroads. As the world grapples with the need for sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions, coal energy presents significant challenges that must be addressed for a successful transition into clean energy alternatives.
One of the foremost challenges in the future of coal lies in its environmental impact. Traditional coal power plants emit substantial amounts of pollutants, including greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change and air pollution. This necessitates the development and implementation of advanced technologies to reduce emissions and minimize the environmental footprint associated with coal energy production.
Furthermore, the global shift toward clean energy sources presents economic challenges for the coal industry. As renewable energy technologies become more cost-effective and widely available, the demand for coal has decreased. This transition requires careful considerations regarding the economic viability of the coal sector, especially in regions heavily reliant on coal mining and power generation.
- Research and development efforts
- Investments in clean coal technologies
- Government policies and regulations
- Transition support for coal-dependent communities
- Integration of renewable energy sources into the grid
The transition to clean energy from coal also necessitates a shift in mindset and workforce adaptation. The workforce employed in the coal industry will need to be reskilled and trained for jobs in the emerging clean energy sectors. This requires collaboration between government, industry, and educational institutions to provide the necessary training and support for a smooth transition.
Despite the challenges, numerous initiatives and technologies offer hope for the future of coal. Efforts to develop and implement clean coal technologies, such as carbon capture and storage, aim to reduce emissions and mitigate environmental impacts. Additionally, investments in renewable energy sources and infrastructure provide opportunities for a sustainable energy future that is free from the enigma and environmental concerns associated with traditional coal extraction and combustion.
In conclusion, the future of coal is undergoing profound changes, driven by the need for cleaner energy alternatives and the growing concerns regarding its environmental impact. Addressing the challenges associated with coal, including emissions reduction, economic viability, and workforce transition, is crucial for a successful transition to clean energy. By embracing technological advancements and fostering collaboration between various stakeholders, a future where coal is no longer synonymous with darkness but rather a stepping stone towards a cleaner and brighter energy landscape is within reach.
FAQ
What is the significance of coal in the dark world?
Coal holds great significance in the dark world as it symbolizes the energy and power hidden within the depths. It is often associated with strength and transformation, representing both the destructive and constructive aspects of life.
What are some common interpretations of dreaming about black coal?
Dreaming about black coal can have various interpretations depending on the context. It may signify a need for inner strength and resilience, or it could indicate the presence of hidden potential and opportunities for growth. It may also symbolize the need to confront and overcome challenges in one's life.
Is there any cultural significance of black coal in dreams?
Black coal holds cultural significance in many societies. For instance, in some folkloric traditions, it is believed that dreaming about black coal is a sign of forthcoming abundance and prosperity. In other cultures, it may represent the underworld or the shadow self, calling for exploration of deeper emotions and desires.
Can dreaming about black coal be a negative omen?
Dreaming about black coal does not necessarily indicate a negative omen. While it may represent challenges or difficulties, it is important to consider the overall dream symbolism and personal associations. It could also be seen as an invitation to harness inner strength and tap into hidden potentials for personal growth and transformation.
Are there any specific actions one should take after dreaming about black coal?
The actions to take after dreaming about black coal may vary depending on individual interpretation and personal beliefs. However, it is beneficial to reflect on the emotions and experiences felt in the dream. This can help identify areas of strength or obstacles that need to be addressed in waking life. Engaging in introspection or seeking guidance from a dream interpreter or therapist can also provide valuable insights.
What is the significance of coal in the dark world?
Coal holds great significance in the dark world as it represents the primary source of energy and power. It is a symbol of both prosperity and hazard, embodying the cyclical nature of life and death. The dark world relies heavily on coal for their industry and infrastructure.
How does the dream about black coal reflect our subconscious thoughts?
Dreaming about black coal can reflect various aspects of our subconscious mind. It might symbolize suppressed emotions or desires, hidden potential, or the need to face difficult challenges. The interpretation of such dreams can vary based on personal experiences and emotions associated with coal or the dark world.



