In the ever-evolving realm of science, the human urge to comprehend the intricacies of our existence has led to the exploration of an enchanting phenomenon – the replication of our genetic blueprint. Paralleling one's desire to delve deeper into the mysterious mechanisms behind our very own composition, the notion of having an identical, genetically reproduced version of oneself has long been ingrained in the human psyche.
Embarking on a captivating journey into the realm of genetic duplication, we venture into a domain where ingenuity intertwines with the quest for personal identity, paving the way for profound philosophical contemplations. Through the green-hued lenses of the laboratory, geneticists and biologists strive to unravel the enigma of genetic replication, continuously pushing the boundaries of what might seem impossible.
With each replicated strand of DNA, scientists not only unlock the potential for medical breakthroughs and the betterment of humanity, but also kindle a fascinating discourse on the discrepancies between nature and nurture. As our understanding of genetics expands, we find ourselves pondering the awe-inspiring question of whether our genes determine our destiny, or if there is an intricate interplay between our genetic makeup and the external environment in shaping our individuality.
Within the ethical tsunami that accompanies this advancement in scientific knowledge, we are confronted with moral quandaries, raising concerns about identity, autonomy, and the very nature of what it means to be human. The prospect of cloning undoubtedly ignites a spectrum of emotions, eliciting alarm and curiosity in equal measure. As we navigate the labyrinthine pathways of this contentious topic, we must grapple with the profound ramifications clone existence could have on our societal fabric.
Science Fiction No More: The Reality of Cloning

In this section, we will delve into the astonishing advancements that have transformed the once fantastical idea of cloning into a tangible reality. We will examine the scientific breakthroughs that have brought us closer to unlocking the potential of genetic replication, revolutionizing the world as we know it.
Cloning, which was once confined to the realm of science fiction, has now become a field of study and experimentation, propelled by groundbreaking discoveries and technological advancements. The once unimaginable concept of creating genetically identical copies of living organisms is now within the reach of human capability.
Advances in cloning technology have given rise to a myriad of possibilities, from therapeutic cloning with the potential to cure diseases and regenerate organs, to the cloning of endangered species in an effort to preserve biodiversity. The field of cloning has expanded our understanding of genetics and has opened up new avenues for scientific exploration.
- Embryonic Cloning: This technique involves the creation of an embryo through somatic cell nuclear transfer, where the nucleus of an adult cell is transferred into an egg whose nucleus has been removed. This process allows for the development of a genetically identical organism.
- Reproductive Cloning: In reproductive cloning, the nucleus of a donor cell is extracted and inserted into an egg cell that has had its nucleus removed. The reconstructed egg is then stimulated to develop into an embryo and implanted into a surrogate mother, resulting in the birth of a genetically identical individual.
- Therapeutic Cloning: This type of cloning involves the creation of embryonic stem cells for medical purposes. By cloning an embryo and extracting its stem cells, scientists can develop treatments for debilitating diseases and injuries, potentially transforming the field of regenerative medicine.
However, the reality of cloning also poses ethical dilemmas and complex societal considerations. Questions surrounding the moral implications of cloning humans, the potential for misuse and exploitation, and the impact on individuality and diversity are subjects of ongoing debate.
Nevertheless, the reality of cloning is undeniably captivating, transforming science fiction into science fact. The progress made in this field continues to redefine our understanding of genetics and holds the promise of a future where the limits of replication are pushed even further.
The Ethics Debate: Should Human Cloning Be Permitted?
In the realm of genetic replication, there exists a contentious ethical debate surrounding the question: Should human cloning be allowed? This debate centers on the moral implications, societal impact, and potential risks associated with the replication of individual humans through scientific means.
Advocates in favor of human cloning argue that it holds the potential to revolutionize healthcare by offering breakthrough treatments and organ transplants, as well as providing solutions to infertility for prospective parents. They believe that cloning could pave the way for advancements in medical research and enhance our understanding of genetics.
However, opponents express concerns regarding the violation of individuality, the potential for misuse, and the blurring of ethical boundaries that human cloning may bring about. They argue that cloning infringes upon the uniqueness and dignity of a human being, challenging fundamental principles of identity and individual autonomy.
Furthermore, the implications on family relationships and societal structure are areas of contention. Human cloning might disrupt family dynamics, blur the lines of kinship, and present challenges regarding legal frameworks such as inheritance and succession. The potential for creating a divide between cloned individuals and non-cloned humans also raises important questions about human rights and equality.
As the advancements in genetic replication technology continue to push boundaries, society must grapple with the ethical dilemmas presented by human cloning. Striking a balance between scientific progress and safeguarding individual rights and values necessitates a rigorous examination of the moral, social, and legal implications. Ultimately, the decision on whether to permit human cloning rests on a complex evaluation of the potential benefits and risks, as well as the profound ethical considerations embedded within this thought-provoking debate.
The Cloning Process Unveiled: From Dolly the Sheep to Modern Techniques
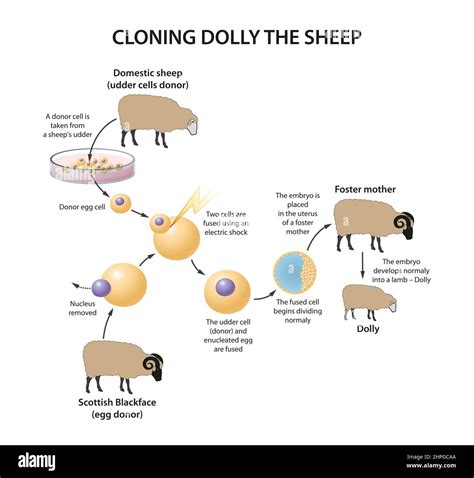
Unraveling the Mystery of Cloning: Exploring the Journey from Dolly the Sheep to Cutting-Edge Methods
In this section, we delve into the fascinating realm of genetic replication, shedding light on the intricate process of cloning. From the groundbreaking creation of Dolly the Sheep to the advancements in modern techniques, we embark on a journey to demystify the complex world of cloning.
1. The Breakthrough: Dolly the Sheep
Our exploration begins with the pioneering success story of Dolly the Sheep, a scientific marvel that captured the world's attention. We dive into the details of this historic achievement, examining the methods employed and the controversies surrounding Dolly's creation. The implications of this breakthrough set the stage for future advancements in cloning techniques.
2. From Nuclear Transfer to Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer (SCNT)
As we progress in understanding the cloning process, we uncover the evolution from the initial nuclear transfer technique to the more refined somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) method. We dissect the steps involved in SCNT, emphasizing the crucial role of specialized cells and the process of reprogramming them to fulfill their potential for creating genetically identical clones.
3. Exploring Embryo Cloning and the Production of Stem Cells
Continuing our exploration, we shift our focus to embryo cloning and its utilization in the production of stem cells. With the use of innovative techniques like cell nuclear replacement, we examine how embryos are created and manipulated to extract pluripotent stem cells, opening doors to groundbreaking research in regenerative medicine.
4. Cloning Techniques: From Animals to Humans
As we approach the conclusion of our journey, we explore the extension of cloning techniques from animals to humans. We discuss the ethical considerations and potential applications of human cloning, highlighting the moral and legal debates surrounding this controversial field.
By the end of this section, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of the cloning process, from its inception with Dolly the Sheep to the recent advancements that have paved the way for new possibilities in the realm of genetic replication.
Cloning Endangered Species: A Solution for Conservation?
Exploring the potential of genetic replication to address the challenges faced by endangered species presents a fascinating avenue for conservation efforts. By harnessing the power of cloning, scientists and conservationists aim to create copies of endangered animals, offering hope for the preservation and restoration of vulnerable populations. This innovative approach holds promise for mitigating the threats posed by habitat loss, poaching, and other factors contributing to the decline of species on the brink of extinction.
Cloning endangered species involves the meticulous replication of an individual's genetic material, allowing for the creation of identical or genetically similar organisms. This technology offers the possibility of reintroducing lost or dwindling populations into their natural habitats, replenishing ecosystems and increasing biodiversity. By duplicating the genetic blueprint of endangered species, scientists seek to combat the irreversible loss of biological diversity and preserve the delicate balance of ecosystems.
Despite its potential benefits, the cloning of endangered species also raises ethical and practical concerns. Critics argue that genetic replication may compromise genetic diversity, as cloned individuals may lack the natural variations necessary for species resilience in the face of changing environments. Furthermore, the high costs and technical challenges associated with cloning hinder its widespread application as a conservation tool.
However, proponents of cloning endangered species emphasize its ability to provide a last resort for species preservation, particularly when other conservation strategies have proven insufficient. Cloning offers a unique opportunity to save species on the brink of extinction, preventing their irreversible disappearance and allowing future generations to appreciate the beauty and diversity of our natural world.
As research and technology continue to advance, the debate surrounding cloning endangered species is sure to evolve. While it is essential to consider the potential drawbacks, it is equally important not to dismiss the possibilities that genetic replication holds for the conservation of biodiversity. With careful regulation and thoughtful implementation, cloning endangered species may serve as a valuable tool in our collective efforts to protect and restore our planet's fragile ecosystems.
The Quest for Perfection: Advancing Genetic Enhancement through Cloning
In this section, we will delve into the ongoing pursuit of achieving perfection through the innovative technique of cloning. By harnessing the power of genetic replication, scientists are exploring new frontiers in elevating the human condition and pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
Unleashing Potential: Cloning for genetic enhancement offers a tantalizing glimpse into a future where individuals have the opportunity to optimize their inherent traits and abilities. By replicating desirable genetic qualities, such as intelligence, athleticism, or longevity, cloning can pave the way for a society where excellence becomes the norm.
Breaking Down Barriers: With the advancement of genetic replication, previously unattainable results can be within reach. The ability to clone genetically superior individuals allows us to challenge limitations imposed by nature, offering hope for overcoming genetic diseases, enhancing intellectual capacities, and pushing the boundaries of the human lifespan.
Ethical Considerations: While the potential benefits of genetic enhancement through cloning are undeniable, it is essential to consider the ethical implications. Discussions surrounding the autonomy of cloned individuals, the potential for inequality, and the blurred lines between natural and engineered traits are crucial in navigating this complex landscape responsibly.
Ushering a New Era: The quest for perfection through cloning for genetic enhancement opens the door to a transformative era in human evolution. By exploring the possibilities and challenges presented by this technology, we are embracing the responsibility to shape a future where the potential of each individual can be fully realized.
The Psychological Impact: The Consequences of Meeting Your Duplicate
Encountering one's genetic replication raises profound psychological questions and engenders a range of complex emotions. The prospect of meeting one's clone can evoke feelings of excitement, curiosity, and even a sense of displacement. This section explores the intricate web of emotions that arises when individuals come face-to-face with their genetic duplicate.
| Emotional & Psychological Responses | Synonyms |
|---|---|
| Awe | Amazement, Wonder, Astonishment |
| Intrigue | Fascination, Interest, Captivation |
| Self-reflection | Introspection, Contemplation, Reflection |
| Identity Crisis | Existential Dilemma, Self-Perception Challenges, Personal Confusion |
| Jealousy | Envy, Resentment, Covetousness |
| Connection | Bond, Rapport, Affiliation |
One prevalent emotional response upon meeting a clone is awe. Witnessing someone who possesses identical genetic material can be astonishing, evoking a profound sense of amazement and wonder. The sheer intrigue of encountering a person with an identical genetic blueprint is enough to captivate one's attention and stimulate a curiosity to delve deeper into understanding the implications of such a meeting.
However, beyond the initial fascination lies a deeper level of self-reflection. Individuals may find themselves engaging in profound introspection, contemplating their own existence and purpose. The encounter with a clone can prompt a personal and philosophical exploration of identity, potentially leading to an existential dilemma or challenges in self-perception.
Jealousy may also emerge as a complicated emotional response when confronted with one's genetic duplicate. Seeing someone who possesses the same genetic advantages can trigger feelings of envy or resentment, causing individuals to question their own uniqueness and place in the world.
On the other hand, the encounter may also foster a deep sense of connection. Meeting one's clone can create a unique bond and rapport, as though they share an instant affiliation. The shared genetic makeup provides a foundation for understanding and a potential source of support and companionship.
The psychological impact of encountering one's clone is a multifaceted and nuanced experience. It encompasses awe, intrigue, self-reflection, jealousy, and the potential for connection. Understanding these complex emotions is vital for comprehending the profound implications that genetic replication holds for individuals and society as a whole.
Beyond Physical Duplication: Unveiling the Boundaries of Mind Cloning

Expanding upon the realms of genetic replication, a remarkable concept emerges: the possibility of duplicating not only the physical attributes but also the intricate workings of the human mind. While the field of genetic replication has captivated scientists and researchers for years, delving into the unexplored territories of mind cloning opens up a universe of endless possibilities and profound ethical implications.
Immerse yourself in this thought-provoking journey as we navigate the uncharted waters of mind cloning. Delving beyond the confines of physical matter, we delve into the realm of consciousness duplication, exploring the potential replication of intellectual capabilities, emotions, memories, and personal experiences.
One avenue of exploration within mind cloning encompasses the fascinating imitation of cognitive processes. Imagine a world where one's intellectual capacity, creativity, and problem-solving abilities are replicated to near perfection. Dive into the depths of neuroscientific research and artificial intelligence advancements that contribute to unraveling the intricate tapestry of the human mind.
Furthermore, delving into the realm of emotional replication poses thought-provoking questions regarding the essence of consciousness. Could it be possible to recreate the complexity of human emotions, harnessing their intensity and subtlety? Explore the moral and philosophical dilemmas tied to the replication of deeply personal sentiments and the potential consequences of tampering with the delicate equilibrium of our emotional makeup.
Yet another aspect to consider is the replication of memories and personal experiences. Venture into the wonders of neuroscience as we unravel the secrets behind memory formation and retrieval. Contemplate the possibilities of preserving and reproducing individuals' most poignant moments, as well as the profound ethical implications that arise when tinkering with the essence of personal identity.
As we embark on this odyssey of mind cloning, be prepared to be captivated by the myriad of questions it raises: What are the limits of consciousness replication? How will society grapple with the moral implications of mind cloning? Can we truly replicate the essence of individuality? Journey with us through the boundless realm of mind cloning and unlock the unexplored frontiers of scientific possibility.
Legal Aspects: Cloning Laws and Regulations Around the Globe
In this section, we will delve into the legal aspects surrounding the subject of genetic replication. Throughout the world, governments and authorities have established a framework of laws and regulations to govern the practice of cloning. These laws aim to ensure ethical considerations, protect the rights of individuals, and preserve the balance between scientific progress and potential risks.
Cloning legislation varies extensively among different countries and regions, reflecting diverse cultural, societal, and religious values. Some nations have embraced a permissive approach, allowing certain types of cloning for research purposes, while others have adopted strict prohibitions on cloning in all forms. It is important to examine the different laws and regulations to understand the global landscape surrounding cloning.
- United States: The United States has a complex legal framework regarding cloning. While federal regulations restrict the use of federal funds for human cloning, there is no blanket federal law prohibiting all forms of cloning. Instead, cloning regulations are primarily governed at the state level, with some states allowing therapeutic cloning for research.
- European Union: The European Union takes a cautious approach to cloning. In 1997, the EU adopted a directive that bans the cloning of human beings, emphasizing the respect for dignity and integrity of the person. The directive also prohibits the patenting of human embryos and cloning methods. However, there is no unified stance on therapeutic cloning, with some member states prohibiting it while others permit it under strict conditions.
- China: China has relatively lenient regulations on cloning. In 2003, the country implemented specific guidelines that allow limited research cloning on embryos under 14 days old. However, reproductive cloning, which aims to create a cloned human being, is strictly prohibited. These regulations reflect a balancing act between advancing scientific research and the maintenance of ethical boundaries.
- Australia: Australia prohibits human reproductive cloning but allows certain forms of therapeutic cloning. The country has a comprehensive framework of laws that regulate cloning research and sets stringent requirements for obtaining licenses to conduct such research.
It is essential to understand the different legal frameworks governing cloning across the globe. These regulations not only reflect the evolution of scientific knowledge and ethical considerations but also shape the boundary between the potential benefits and inherent concerns associated with genetic replication.
The Future of Cloning: Embracing New Horizons for Humanity
As we voyage deeper into the uncharted realm of genetic advancements, the concept of cloning has emerged as a captivating prospect with immense potential for the future of mankind. This thought-provoking arena brings forth a myriad of possibilities, showcasing the remarkable prospects and implications that cloning could bestow upon our society.
Unveiling the Boundless Potential
Cloning, as an increasingly accessible technology, has the power to unlock incredible opportunities in various fields of human existence. From revolutionizing medical treatments and therapies to addressing environmental challenges and conserving endangered species, the profound impact of cloning promises to surpass conventional boundaries.
Redefined Notions of Identity and Individuality
With the advent of cloning, long-held conceptions surrounding our identity and individuality are bound to be reevaluated. Cloned individuals would bring forth fascinating ethical and philosophical inquiries, compelling us to reassess the intricate tapestry of human existence and the very essence of what it means to be human.
Overcoming Biological Limitations
The future of cloning holds the potential to conquer the limitations of the human body, enabling us to overcome genetic diseases, extend our lifespan, and enhance our physical and mental capabilities. By harnessing the power of genetic replication, humanity may embrace a new era of improved health and well-being.
Navigating Ethical Considerations
As we journey into the unexplored territories of cloning, we must tread carefully and address the complex web of ethical considerations woven within this field. Ensuring that the rights and dignity of cloned individuals are honored will play a vital role in shaping the ethical foundations of a cloning-centric future.
Charting Unknown Territories
As we embark on this thought-provoking exploration of cloning, it becomes evident that the future holds a vast expanse of uncharted territories. The possibilities and challenges that lie ahead compel us to embrace open dialogue, rigorous ethical analysis, and a steadfast commitment to ensure that the future of cloning serves the betterment of humanity.
FAQ
What is genetic replication?
Genetic replication refers to the process of creating an organism with an identical genetic makeup to another existing organism. It involves copying the DNA of the original organism and producing an exact replica.
Is it currently possible to clone humans?
No, it is not currently possible to clone humans. Despite advancements in genetic technology, human cloning is still considered ethically and morally controversial, and there are legal restrictions in place in most countries.
Why do some people dream of being cloned?
Some people may dream of being cloned as a way to extend their existence or to experience life from a different perspective. It can also be related to a desire for immortality or the fear of death.
What are the potential risks and dangers of genetic replication?
The potential risks and dangers of genetic replication include the possibility of genetic abnormalities or mutations in the cloned organism, as well as potential psychological and emotional issues that may arise from being a clone. Additionally, there are concerns about the infringement of individuality and the ethical implications of creating human life through cloning.
Are there any benefits to genetic replication?
Genetic replication can have potential benefits in fields such as medical research and organ transplantation. Cloning can be used to create genetically identical animals for scientific experiments, leading to advancements in understanding diseases and developing new treatments.
What is genetic replication?
Genetic replication is the process of creating an exact copy of an organism's DNA, resulting in the production of a genetically identical individual. It involves duplicating the genetic material, including all the genes and sequences, to create an identical offspring.



