During the mystical hours of the night, when the mind ventures into realms unknown, our nocturnal experiences can sometimes be filled with unexpected tribulations. In these ethereal wanderings, our bodies may be subjected to puzzling disconcertions, whispers of the hidden workings of our subconscious. One such enigmatic obstacle that may manifest in our dreams is an auricular disturbance, an elusive and discomforting encounter which leaves us searching for answers upon awakening.
Reverberating within the chambers of the dream world, this perplexing predicament elicits a cloak of intrigue, demanding our attention to unravel its origins and implications. Though bereft of its explicit designation, we embark on a journey to understand the torment that insidiously infiltrates our nocturnal solitudes.
Clasped within the enigmatic embrace of this nighttime ordeal, the sleep-laden mind feels the echoes of a clandestine struggle, unknowingly grappling with the somnolent negotiations of its auricular realm. As eyes flutter in slumber, unconscious tastes the reverberations of sound, hushed whispers of a symphony played within, where harmony gives way to dissonant tones. In these subconscious moments, the introspective self is besieged with sensations that mimic the signs of an uninvited auricular trespasser.
The Common Causes of Otitis
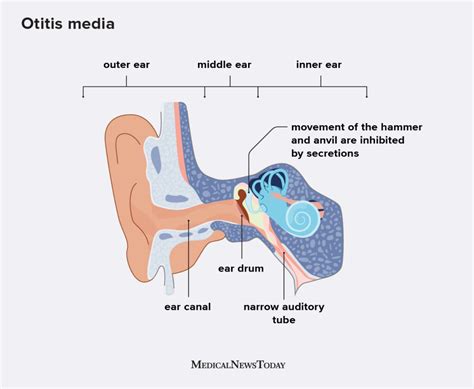
When it comes to the roots of otitis, the reasons behind this common ear condition are varied and can be attributed to a range of factors. Understanding the causes of otitis is essential in preventing and effectively treating this discomforting ailment.
- Bacterial Infections: One common cause of otitis is bacterial infection. Certain bacteria, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae, can infiltrate the ear canal and lead to inflammation and infection.
- Viral Infections: Viruses can also play a role in the development of otitis. Respiratory viruses, including the common cold and flu, can travel from the upper respiratory tract to the middle ear, resulting in infection.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions can contribute to the onset of otitis. When the body's immune system reacts to allergens, such as pollen or pet dander, it can cause inflammation and fluid buildup in the middle ear, creating a favorable environment for the growth of bacteria or viruses.
- Blocked Eustachian Tube: The Eustachian tube, which connects the middle ear to the back of the throat, plays a crucial role in equalizing pressure and draining fluids from the ear. When this tube becomes blocked due to factors like congestion from a cold or sinus infection, it can disrupt normal ear function and increase the risk of infection.
- Swimming: Spending time in water can also contribute to the development of otitis. Excessive moisture in the ear can create an ideal breeding ground for bacteria, leading to infection commonly known as "swimmer's ear."
- Anatomy: Certain anatomical factors can make individuals more prone to ear infections. For example, infants and young children are at higher risk due to their shorter, horizontal Eustachian tubes, which are more easily blocked.
By understanding the common causes of otitis, individuals can take proactive measures to prevent infection, such as practicing good hygiene, avoiding allergens, and addressing underlying respiratory conditions. If symptoms arise, seeking prompt medical attention can aid in early diagnosis and appropriate treatment to alleviate discomfort and prevent complications.
Recognizing the Signs of an Aural Inflammation
Identifying the symptoms of an ear infection is crucial in order to initiate prompt treatment. These symptoms manifest through various indicators and can differ from person to person. By becoming aware of these signs, individuals can quickly identify whether they are experiencing an infection within the auditory system.
- Earache or discomfort: A common symptom is the presence of pain or discomfort in the ear. This sensation may range from mild to severe and can be continuous or intermittent.
- Changes in hearing: Those affected by an ear infection may experience a decrease in their ability to hear or notice a muffled sound in their affected ear.
- Feeling of pressure: Some individuals may perceive a sensation of fullness or pressure within the ear, similar to the feeling of having the ear plugged.
- Fluid drainage: In some cases, a yellow or white fluid may drain from the affected ear. This discharge can be accompanied by a foul odor.
- Redness and swelling: The outer ear or the area behind the ear may appear red, swollen, or tender to touch, indicating an inflammatory response.
- Fever: Especially in children, an ear infection may be accompanied by a slight increase in body temperature, resulting in a low-grade fever.
- Dizziness or balance issues: Some individuals may experience dizziness, vertigo, or difficulties with balance due to an ear infection affecting the inner ear.
Understanding these symptoms can help individuals recognize and seek appropriate medical attention for a potential ear infection. It is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Ear Infections
When faced with the challenge of treating an ear infection, there are several options available to alleviate the discomfort and promote healing. These approaches aim to tackle the underlying causes and provide relief from the symptoms associated with this condition.
- Antibiotics: One common treatment option for ear infections involves the use of antibiotics. These medications are prescribed to combat bacterial infections that may be contributing to the problem. They work by targeting and killing the bacteria responsible for the infection, allowing the body to recover.
- Pain relief: Ear infections often cause significant pain and discomfort. To relieve these symptoms, over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can be used. Applying warm compresses to the affected area may also help to alleviate pain and reduce swelling.
- Ear drops: Another treatment option involves the use of ear drops specifically formulated to treat ear infections. These drops are typically composed of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications. They are administered directly into the ear canal to combat the infection and reduce inflammation.
- Home remedies: Some individuals prefer to explore natural and home remedies to treat ear infections. These remedies may include the use of warm olive oil or garlic oil drops, which are believed to have antimicrobial properties. Additionally, applying a warm towel or using a humidifier can help to soothe the discomfort associated with ear infections.
- Surgical intervention: In severe cases or when other treatment methods fail to provide relief, surgical intervention may be necessary. This could involve a procedure known as a myringotomy, where a small incision is made in the eardrum to drain fluid and relieve pressure. Tubes may also be inserted into the ears to promote proper drainage and prevent future infections.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable treatment option based on the severity of the infection, individual needs, and medical history. In some instances, a combination of different approaches may be recommended for optimal results.
FAQ
What are the common causes of an ear infection?
An ear infection can be caused by various factors such as respiratory infections, allergies, excessive earwax buildup, and changes in air pressure.
How do I know if I have an ear infection?
Common symptoms of an ear infection include ear pain, fluid drainage from the ear, hearing loss, difficulty sleeping, and dizziness.
Can ear infections affect both children and adults?
Yes, ear infections can affect individuals of all ages. However, children are more prone to ear infections due to their underdeveloped Eustachian tubes.
What are the treatment options for an ear infection?
Treatment for an ear infection depends on the severity and underlying cause. It may include over-the-counter pain relievers, prescription antibiotics, or in some cases, surgical intervention.
Is it possible for ear infections to recur?
Yes, it is possible for ear infections to recur, especially if the underlying cause is not properly addressed. Recurrent ear infections may require further investigation and management by a healthcare professional.
What are the common causes of an ear infection?
An ear infection can be caused by several factors, including respiratory infections, allergies, sinus infections, excessive moisture in the ear, and a weakened immune system.
What are the symptoms of an ear infection?
The symptoms of an ear infection may include ear pain, headache, muffled hearing, fluid drainage from the ear, fever, trouble sleeping, and irritability in children.



