Are you yearning for a flawless complexion devoid of chromatic inconsistencies? Discover the hidden complexities behind the illusion of clear and unadulterated skin. The human integumentary system, an intricate and multifaceted organ, serves as our shield from external threats. However, beneath its seemingly impervious facade lies an array of unsuspected adversaries, capable of leaving behind faint, discolored marks. This article delves into the enigmatic realm of ethereal discolorations, exploring the underlying causes, unmistakable signs, and effective protocols for their treatment.
Within the realm of this perplexing anomaly, an assortment of contributing factors emerges from the depths of the epidermis. Some potential instigators may encompass genetic predispositions, environmental triggers, or even the result of certain illnesses. These latent catalysts conceal themselves within the very foundation of our dermis, silently orchestrating the emergence of pale blotches that quash our cherished desires for a uniform complexion. As we strive to unravel the complexity of this enigma, it becomes evident that no single cause can singularly claim responsibility for these elusive depigmented patches.
Recognizing the symptoms associated with these unsuspecting visitors is paramount in our quest for rejuvenated dermal health. As an individual watches their melanin diminish before their very eyes, their once vibrant and vivid skin tone succumbs to the gradual encroachment of ashen discolorations. The loss of color may vary in intensity, ranging from barely discernible to strikingly apparent. The affected areas may possess a distinctive texture, deviating from the smooth, supple nature of their unaffected counterparts. Awareness and comprehension of these unmistakable signs play a pivotal role in seeking accurate diagnosis and tailoring the ideal course of action.
Understanding Hypopigmentation: What Causes White Patches on Skin?
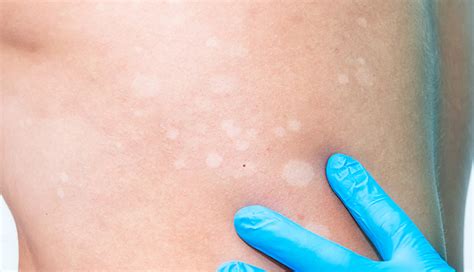
When it comes to changes in skin color, hypopigmentation is an intriguing condition that often raises questions. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of the causes behind the appearance of white patches on the skin, taking a closer look at the underlying factors responsible for hypopigmentation.
Hypopigmentation occurs when there is a decrease in the production or distribution of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin, hair, and eye color. The lack of melanin in certain areas can result in the formation of white patches on the skin, sometimes referred to as depigmentation.
- Genetic Factors - In some cases, hypopigmentation can be inherited and passed on from generation to generation. Certain genetic conditions, such as albinism and vitiligo, can cause reduced melanin production, leading to noticeable white patches on the skin.
- Skin Infections and Inflammation - Skin infections, such as tinea versicolor or pityriasis alba, can disrupt the normal pigmentation process, resulting in the formation of white patches. Additionally, inflammatory skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis can also lead to hypopigmentation in affected areas.
- Autoimmune Disorders - Some autoimmune disorders, such as lupus or scleroderma, can trigger an immune response that mistakenly attacks the pigment-producing cells in the skin. This immune reaction can result in the loss of melanin and the appearance of white patches.
- Chemical Exposure and Trauma - Certain chemicals, such as bleach or certain medications, can cause skin damage and subsequent hypopigmentation. Additionally, injuries, burns, or scars can disrupt the normal melanin production process, leading to the formation of white patches.
- Sun Exposure - While excessive sun exposure is often associated with darkening of the skin, it can also contribute to hypopigmentation. Prolonged UV radiation can damage the melanocytes, leading to a loss of melanin and the development of white patches.
Understanding the various causes of hypopigmentation is crucial in developing effective treatment approaches. While there is no universal cure for all cases of hypopigmentation, treatments may include topical creams, phototherapy, micropigmentation, or surgical interventions, depending on the specific underlying cause and individual circumstances.
It is important to consult a dermatologist or healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan tailored to address the specific causes and symptoms of individual cases of hypopigmentation.
Spotting the Signs: Symptoms of Pale Spots on the Epidermis
Wondering how to recognize the presence of pale patches on your skin? The human body exhibits various indicators that could be suggestive of the existence of hypopigmentation. By understanding and observing these symptoms, individuals can achieve early detection and prompt treatment to address any potential underlying conditions.
One of the key signs of pale spots on the skin is depigmentation, which refers to the loss of melanin, the pigment responsible for determining skin color. Hypopigmentation can manifest as lighter patches, contrasting with the person's overall skin tone. These patches may appear randomly or in specific regions, such as the face, arms, or legs.
An additional indicator to be on the lookout for is the presence of white patches accompanied by itching or dryness. These symptoms can be uncomfortable and potentially distressing. If you experience itching or dryness alongside the appearance of pale spots, it is advisable to seek medical attention to rule out any underlying conditions or infections.
In some cases, individuals may notice a gradual expansion of the pale areas over time. This progressive growth can be a further sign of hypopigmentation. Observing any changes in the size, shape, or coloration of the patches is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Sensitivity to sunlight is yet another symptom that may accompany the presence of white patches on the epidermis. Individuals with hypopigmentation may find that their affected areas are more prone to sunburn or exhibit a heightened sensitivity to UV rays. Protecting these areas with appropriate sun protection measures is essential for maintaining skin health and preventing further damage.
If you notice any of these symptoms or have concerns about the appearance of pale patches on your skin, it is recommended to consult a qualified healthcare professional. They can examine your specific symptoms in detail, provide a proper diagnosis, and outline the most suitable treatment options to address the underlying cause of the condition.
Exploring Underlying Conditions Associated with Hypopigmentation
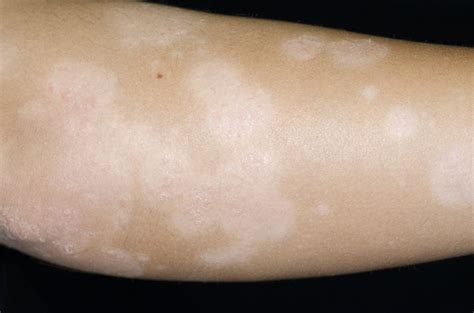
Delving deeper into the realm of skin pigmentation, it is crucial to recognize the vast array of underlying conditions that can be linked to hypopigmentation. Beyond the surface, these conditions reveal a complex interplay of factors that contribute to the development of white patches on the skin.
1. Vitiligo: This autoimmune disorder manifests as the destruction of melanocytes, leading to the loss of pigment in the skin. Though the exact cause remains unknown, genetic predisposition and environmental factors can contribute to the development of vitiligo.
2. Albinism: Albinism is a genetic condition characterized by the absence of melanin production, resulting in a complete lack of pigmentation in the skin, hair, and eyes. Albinism may be inherited and is associated with various genetic mutations.
3. Tinea Versicolor: This common fungal infection is caused by Malassezia furfur, which disrupts the normal pigmentation process. The resulting hypopigmentation can manifest as light-colored patches on the skin. Factors such as heat, humidity, and oily skin can contribute to the development of tinea versicolor.
4. Post-inflammatory Hypopigmentation: Certain skin conditions, such as eczema, psoriasis, or burns, can trigger an inflammatory response that damages melanocytes. This can lead to hypopigmentation in the affected areas as the skin heals.
5. Halo Nevus: This benign skin lesion is characterized by a depigmented ring surrounding a mole. The exact cause of halo nevus is unknown, but it is believed to be an immune-mediated response targeting the melanocytes within the mole.
Understanding the underlying conditions associated with hypopigmentation is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. By exploring these factors, medical professionals can provide comprehensive care to individuals with white patches on their skin.
Unveiling Solutions: How to Treat Discolored Areas on the Skin
When faced with changes in pigmentation on the body's outer layer, it's important to understand the various options available for addressing these discolored areas. By exploring effective treatment methods, individuals can regain their confidence and restore an even complexion.
One of the common solutions for managing pigmentation issues involves topical creams and ointments. These products are formulated with specific ingredients to target the underlying cause of the skin discoloration. By regularly applying these creams, individuals can gradually restore balance to their complexion.
Another effective treatment option is phototherapy or light therapy. This method utilizes different types of light, such as UVB rays, to stimulate melanocytes in the skin, promoting the production of melanin. This can help even out the skin tone and reduce the appearance of white patches over time.
In more severe cases, surgical interventions may be considered. Skin grafting, for example, involves replacing the affected area with healthy skin from another part of the body. This procedure allows for the transplantation of melanocytes, which can help restore natural pigmentation to the discolored patches.
Additionally, lifestyle modifications can play a role in managing white patches on the skin. Maintaining a healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin D, vitamin B12, and folic acid, can support the body's natural healing processes. Engaging in stress-reducing activities, like yoga or meditation, may also contribute to overall skin health.
It's important to note that the most effective treatment option will vary depending on the individual and the underlying cause of the pigmentation issues. Consulting with a dermatologist or healthcare professional is crucial to determine the most suitable approach for each unique case.
| Treatment Methods | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Topical Creams and Ointments | - Non-invasive option - Gradual restoration of pigmentation | - Results may take time - Potential side effects |
| Phototherapy | - Effective for even skin tone - Stimulates melanin production | - Requires multiple sessions - Possible skin sensitivity |
| Surgical Interventions | - Allows for precise treatment - Restores natural pigmentation | - Invasive procedure - Risk of complications |
Exploring Medical Interventions: Procedures for Treating Hypopigmentation
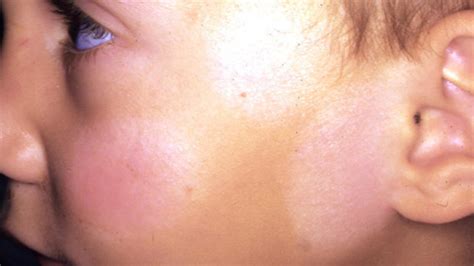
In this section, we will delve into various medical interventions aimed at addressing the condition of hypopigmentation. By exploring different procedures, we will examine the approaches taken by healthcare professionals to restore the natural pigmentation of the skin. Through these interventions, individuals with hypopigmented patches can regain their skin's color and improve its overall appearance.
1. Topical Treatments:
- Prescribed creams or ointments that contain corticosteroids are often used to reduce inflammation and encourage the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color.
- Another option is the application of topical immunomodulators, which can help restore pigmentation by regulating the immune response within the skin.
2. Micropigmentation:
- Micropigmentation, also known as cosmetic tattooing, involves inserting pigment into the skin to mimic the appearance of natural pigment. This procedure is commonly used to address hypopigmentation in areas such as the lips, eyebrows, and areolas.
- With the help of specialized equipment, a skilled technician carefully matches the pigment to the patient's desired skin tone, creating a natural-looking result.
3. Laser Therapy:
- Laser therapy utilizes high-energy light beams to target areas of hypopigmentation. The laser light stimulates the production of melanin, promoting the growth of pigmented cells in the affected areas.
- This non-invasive procedure can help even out skin tone and reduce the appearance of white patches over time.
4. Surgical Interventions:
- In more severe cases of hypopigmentation, surgical procedures may be recommended. One such procedure is punch grafting, which involves removing small pieces of pigmented skin from one area of the body and transplanting them onto the hypopigmented areas.
- Another surgical option is autologous melanocyte transplantation, where melanocytes (cells responsible for producing melanin) are extracted from the patient's healthy skin and transplanted onto the affected areas.
It is important to note that the most suitable intervention for treating hypopigmentation varies depending on the individual's specific condition and the recommendations of a healthcare professional. By exploring these medical procedures, individuals can gain a better understanding of the available options and make informed decisions regarding their treatment.
Boosting Confidence: Strategies for Coping with Hypopigmentation
Living with hypopigmentation can pose challenges to a person's self-confidence and body image. However, there are various coping strategies that individuals with hypopigmentation can employ to boost their self-esteem and feel more comfortable in their own skin.
1. Embracing Individuality: Recognize that your hypopigmentation is a unique feature that sets you apart from others. Instead of viewing it as a flaw, embrace it as a part of your individuality and beauty.
2. Building a Support System: Surround yourself with people who uplift you and accept you for who you are. Having a strong support system of friends and family can provide you with the reassurance and encouragement you need to feel confident and comfortable in your own skin.
3. Educating Yourself: Learn more about hypopigmentation and its causes so that you can better understand and explain it to others. Educating yourself about your condition can empower you and give you the tools to advocate for yourself when facing misconceptions or discrimination.
4. Seeking Professional Help: If your hypopigmentation is causing significant distress, consider seeking professional help. A dermatologist or counselor can provide guidance, support, and possible treatment options to improve your self-confidence.
5. Practicing Self-Care: Prioritize self-care activities that make you feel good about yourself. Engage in activities such as exercising, practicing mindfulness, or pursuing hobbies that boost your mood and overall well-being.
6. Enhancing Appearance: Experiment with makeup, clothing, and accessories that complement your unique skin tone. Enhancing your appearance can help you feel more confident and comfortable in social situations.
7. Advocacy and Awareness: Get involved in advocacy efforts to raise awareness about hypopigmentation and promote inclusivity. By becoming an advocate, you can help educate others and contribute to a more accepting and understanding society.
In conclusion, individuals with hypopigmentation can adopt coping strategies to boost their self-confidence and develop a positive body image. By embracing their individuality, building a support system, educating themselves, seeking professional help if needed, practicing self-care, enhancing their appearance, and becoming advocates for change, they can navigate through life with confidence and pride.
FAQ
What are the causes of white patches on the skin?
White patches on the skin can be caused by various factors including vitiligo, a condition where the immune system attacks the melanin-producing cells, resulting in loss of pigmentation. Other causes can include fungal infections, autoimmune diseases, sunburn, and certain medications.
What are the symptoms of white patches on the skin?
The symptoms of white patches on the skin can vary depending on the underlying cause. In cases of vitiligo, the patches are usually depigmented, smooth, and well-defined. There may also be a loss of color in the hair and inner lining of the mouth. Other symptoms can include itching, redness, inflammation, or pain.
Is there a cure for white patches on the skin?
While there is currently no known cure for vitiligo, there are treatment options available to help manage and improve the appearance of white patches on the skin. These can include topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, phototherapy, skin grafting, and depigmentation for widespread vitiligo. Treatment for other causes of white patches will depend on the underlying condition and may involve antifungal medications, immunosuppressants, or lifestyle changes.
Are white patches on the skin a sign of a serious medical condition?
White patches on the skin can be a symptom of various medical conditions, some of which may be serious. It is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment. While vitiligo itself is not harmful or contagious, it can have psychological and emotional impacts on individuals affected by it.



