Delving deep into the enigmatic world of medicolegal investigation, where death and science intertwine, lies an intriguing realm that piques both curiosity and fascination. This captivating domain, shrouded in mystique, is none other than the mortuary - a hallowed space where the secrets of the deceased are unveiled through the meticulous art of forensic medicine.
Within the walls of the mortuary, science and deduction converge to unravel the complex puzzle of life's sudden cessation. It is here that forensic pathologists, armed with keen intellect and a relentless pursuit of truth, piece together the intricate clues left behind by the deceased. With every examination, a narrative unfolds, painting a vivid picture of events that led to the final chapter of existence.
Under the glare of harsh fluorescent lights, the solemn atmosphere permeates the air, as each and every cadaver tells a tale. Every step taken within these hallowed halls is a glimpse into the labyrinth of human mortality. From the meticulous dissection of the deceased's anatomy to the analysis of chemical markers within their body, forensic medicine illuminates the darkest corners of our mortality.
Within this captivating journey of exploration, the utmost precision is essential. Doctors and specialists work hand in hand, utilizing state-of-the-art equipment and cutting-edge techniques to extract truth from the silent remains. It is in this crucible of knowledge that the mysteries surrounding death find their resolution, bringing closure to grieving families and justice to those who have met an untimely demise.
As we embark on this enthralling odyssey through the mortuary, be prepared to witness the convergence of science and deduction, truth and mystery, in a symphony that captivates the imagination. The realm of forensic medicine beckons, inviting those with an insatiable thirst for knowledge to uncover the secrets hidden within the silent chambers of the departed.
The Role of Forensic Medicine in Crime Solution
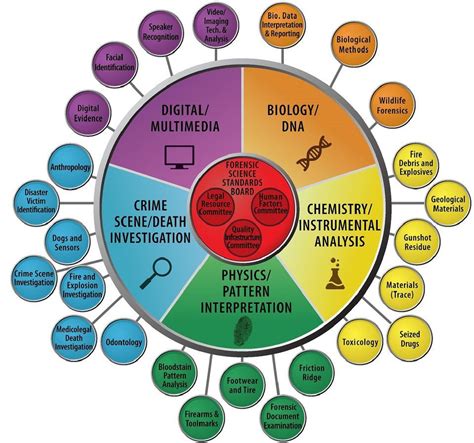
Forensic medicine plays a pivotal role in the investigation and resolution of criminal cases by providing scientific and medical expertise to aid in the determination of cause and manner of death, identification of victims, and the evaluation of physical evidence.
One of the primary responsibilities of forensic medicine is to conduct autopsies, which involve the systematic examination of deceased individuals to uncover essential information about the circumstances surrounding their death. Through careful examination and analysis, forensic pathologists can determine the cause of death, whether it be natural, accidental, suicidal, or homicidal, providing critical insights into the investigation of potential crimes.
In addition to autopsies, forensic medicine utilizes various techniques and methods to identify victims. From fingerprint analysis, dental records, and DNA testing to facial reconstruction and anthropological examination, forensic experts employ a wide range of scientific approaches to establish the identity of individuals. This aspect of forensic medicine plays a crucial role in ensuring justice and providing closure to families and loved ones.
Moreover, forensic medicine examines physical evidence found at crime scenes, such as bloodstains, clothing fibers, and bullets, in order to reconstruct the events leading to a crime. By analyzing these pieces of evidence using advanced scientific techniques, forensic experts can link suspects to the crime, establish timelines, and provide vital information to investigative authorities.
Furthermore, forensic medicine plays a vital role in analyzing and interpreting toxicology reports. By examining bodily fluids and tissues, forensic toxicologists can identify the presence of drugs, alcohol, or other substances, shedding light on the potential influence these substances may have had on the events leading to a crime. This information is crucial in determining motive, intent, and culpability.
In summary, forensic medicine serves as an indispensable tool in the resolution of criminal cases. Through autopsies, victim identification, analysis of physical evidence, and interpretation of toxicology reports, forensic experts provide invaluable insights into the circumstances surrounding crimes, aiding law enforcement agencies in their quest for justice and truth.
Exploring the Science behind Forensic Pathology
Delving into the underlying principles of forensic pathology unveils a captivating world that merges medical expertise with scientific investigation. This branch of pathology involves the comprehensive examination and analysis of deceased individuals to determine the cause and manner of death, providing crucial insights into criminal investigations and legal proceedings.
Forensic pathologists, also known as medical examiners, employ their knowledge of anatomy, physiology, and pathology to examine the deceased's body externally and internally, meticulously documenting any injuries, disease processes, or abnormalities. Through detailed analysis, they strive to recreate the events leading to the individual's demise and provide an objective assessment of the circumstances surrounding their death.
One fundamental aspect of forensic pathology is the determination of the cause of death, which involves careful examination and interpretation of various factors such as injuries, toxicology reports, and medical records. This process requires a comprehensive understanding of human anatomy and the ability to recognize and interpret subtle signs of trauma or disease.
The examination of organs and tissues extracted during autopsies is another critical component of forensic pathology. This meticulous investigation often involves the dissection and sampling of organs, aiming to uncover any underlying pathology that may have contributed to the individual's death. Microscopic examination of tissue sections allows pathologists to identify diseases or conditions not visible to the naked eye.
Forensic pathologists also play a vital role in the field of forensic anthropology, assisting in the identification of skeletal remains. By analyzing bone structure and assessing various skeletal features, they can determine an individual's age, sex, and potentially contribute to establishing their identity.
In addition to conducting autopsies and analyzing evidence, forensic pathologists are responsible for meticulously documenting their findings and presenting them in a court of law. They must possess excellent communication skills and convey complex medical information in a clear and understandable manner to attorneys, judges, and juries.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Forensic pathology involves the examination and analysis of deceased individuals to determine the cause and manner of death. |
| Forensic pathologists employ their knowledge of anatomy, physiology, and pathology to meticulously document injuries, disease processes, and abnormalities. |
| Determining the cause of death requires a comprehensive understanding of human anatomy and the interpretation of various factors. |
| The examination of organs and tissues extracted during autopsies aims to uncover any underlying pathology contributing to the individual's death. |
| Forensic pathologists also contribute to the field of forensic anthropology, assisting in the identification of skeletal remains. |
| Forensic pathologists must possess excellent communication skills to present their findings in a court of law. |
Revealing the Mysteries of Autopsy Procedures
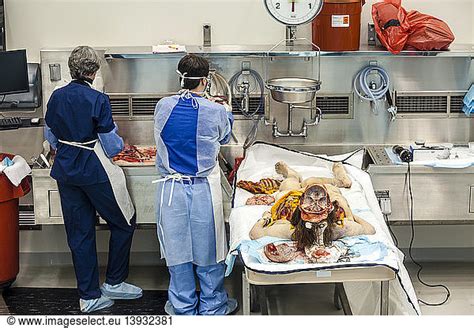
In this section, we will explore the fascinating world of autopsy procedures and delve into the intricate process through which forensic pathologists unravel the mysteries surrounding a person's cause of death. Here, we will uncover the secrets behind the meticulous examination of the deceased, the collection of crucial evidence, and the wealth of knowledge gained to aid in criminal investigations or uncover the truth behind medical conditions.
1. The Initial Examination: At the beginning of an autopsy, the body is meticulously inspected externally to gather vital information. This includes observing any visible injuries, identifying distinguishing marks, and documenting relevant characteristics such as age, height, and weight. Additionally, photographs and X-rays may be taken to assist in further analysis. |
2. Internal Exploration: Following the external examination, a meticulous internal exploration is conducted to unveil the secrets concealed within the body. Forensic pathologists skillfully perform a systematic dissection, examining organs, tissues, and bodily fluids to identify abnormalities, injuries, or diseases that may have contributed to the individual's demise. |
3. Evidence Collection: During the autopsy, vital evidence is collected for further analysis. This can include samples of bodily fluids, tissues, or potential foreign substances that may help identify toxins, drugs, or even DNA evidence. The careful preservation and documentation of these samples facilitate the accurate reconstruction of events and contribute to the formation of a complete forensic profile. |
4. Laboratory Analysis: Once the autopsy is complete, the collected evidence undergoes rigorous laboratory analysis. Advanced diagnostic techniques are employed to uncover hidden details, such as toxicology screenings, genetic testing, and histopathological examinations. This multidisciplinary approach aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the circumstances surrounding the individual's death. |
5. Collaboration and Documentation: Forensic pathologists work closely with various professionals, such as law enforcement agencies, medical experts, and legal teams, to interpret findings and draw conclusions. Extensive documentation of the autopsy results, including detailed reports, microscopic images, and diagrams, serves as a vital resource in legal proceedings or further scientific research. |
Through the meticulous process of autopsy procedures, forensic medicine provides invaluable insights into the causes of death, shedding light on complex medical conditions, facilitating criminal investigations, and ultimately enabling justice to prevail.
The Role of DNA in Forensic Medicine: From Identification to Solving Crimes
In the field of forensic medicine, the utilization of DNA has revolutionized the process of identification and crime solving. This section will delve into the significant role that DNA plays in various aspects of forensic investigations, ranging from establishing the identity of individuals to aiding in the resolution of complex criminal cases.
1. Identification: DNA profiling has emerged as a key tool for the identification of individuals in forensic investigations. By comparing the unique genetic markers present in a person's DNA, experts can conclusively determine their identity, even in cases where traditional methods of identification may be challenging or impossible.
2. Familial DNA Searching: In instances where direct matches to DNA profiles are unavailable, familial DNA searching can be employed. This technique allows investigators to identify potential relatives of an unknown DNA sample, increasing the likelihood of uncovering leads and identifying suspects.
3. Forensic DNA Databases: Forensic DNA databases serve as invaluable resources for law enforcement agencies. By storing DNA profiles from convicted offenders, crime scenes, and unidentified bodies, these databases facilitate the linkage of crimes, providing investigative leads and assisting in the solving of cold cases.
4. Forensic DNA Phenotyping: With advancements in technology, forensic DNA phenotyping has emerged as a powerful tool for generating physical descriptions of unknown individuals. By analyzing specific DNA markers associated with physical traits, such as eye color, hair color, and ancestry, forensic scientists can create composite sketches, narrowing down the pool of potential suspects.
5. Forensic Genetics in Criminal Investigations: DNA evidence collected from crime scenes can play a crucial role in criminal investigations. Whether it is through matching DNA from suspects to evidence left at the scene or identifying victims, DNA analysis has helped solve numerous crimes and bring perpetrators to justice.
6. Challenges and Ethical Considerations: While DNA analysis has proven to be a powerful tool in forensic medicine, it is not without its challenges and ethical considerations. Issues such as privacy concerns, the interpretation of DNA evidence, and potential bias must be carefully addressed to ensure the responsible and fair use of DNA technology in criminal investigations.
7. The Future of DNA in Forensic Medicine: The ongoing advancements in DNA technology continue to expand the capabilities of forensic medicine. From improved techniques in sample collection and analysis to the integration of artificial intelligence, the future holds immense potential for further enhancing the impact of DNA in solving crimes and bringing closure to victims and their families.
Unveiling the Secrets: Forensic Anthropology and the Analysis of Bones

Delving into the intriguing world of forensic medicine, one particular branch stands out for its unique ability to uncover hidden clues from skeletal remains. Forensic anthropology, a specialized field within forensic medicine, focuses on the examination and interpretation of bones to aid in the identification of deceased individuals, determine time since death, and unravel the circumstances surrounding a person's demise.
Combining the meticulous examination of skeletal morphology with a keen understanding of human anatomy, forensic anthropologists play a crucial role in forensic investigations. By studying the bones, these experts can piece together crucial information, such as age, sex, stature, and potential signs of trauma or disease. Through these analyses, forensic anthropologists contribute to the development of a comprehensive profile that can assist in the identification of individuals, shed light on their lifestyle and habits, and even provide invaluable insights into potential cause of death.
The Complexity of Bone Analysis
Forensic anthropology involves the examination of bones using a variety of techniques and tools. These include assessment of bone size, shape, and structure, identification of skeletal landmarks, and the examination of growth patterns. By meticulously analyzing these features, forensic anthropologists are able to piece together vital clues about an individual's past.
Unraveling the Age and Sex
One of the primary tasks of a forensic anthropologist is to determine the age and sex of the individual based on their skeletal remains. By examining the fusion of epiphyses, the development of teeth, and the overall bone structure, these experts can estimate an individual's age at the time of death. Similarly, through the assessment of pelvic and cranial features, as well as the presence of specific bone markers, forensic anthropologists can identify the biological sex of the deceased.
Reconstructing the Living Individual
Building upon the initial assessment of age and sex, forensic anthropologists utilize their expertise to reconstruct the individual's lifestyle, health history, and potential traumatic or pathological conditions. By examining the presence of bone fractures, evidence of disease, and the effects of habitual activities such as repetitive motion or manual labor, these experts can gain valuable insights into the daily life and potential occupational hazards faced by the deceased.
Implications in Forensic Investigations
The invaluable contributions of forensic anthropology extend beyond identification and cause of death determinations. This field aids in criminal investigations by providing information on potential abuse, trauma, or violence inflicted upon the individual. Additionally, forensic anthropology plays a crucial role in the recovery of human remains from mass disasters, natural calamities, or war zones, providing closure to families and essential evidence for legal proceedings.
As an indispensable component of the forensic medicine landscape, forensic anthropology continues to captivate researchers, uncover mysteries, and provide invaluable assistance in uncovering the truth from the silent witnesses of the past.
The Significance of Forensic Odontology in Human Remains Identification
Understanding the crucial role of forensic odontology in the identification of human remains is paramount in forensic medicine. This branch of forensic science utilizes dental evidence and expertise to provide invaluable insights into the identification process, particularly in cases where traditional methods may be insufficient or unavailable.
Forensic odontology encompasses the use of dental records, dental radiographs, and bite mark analysis. Dental records, such as dental charts and X-rays, provide a comprehensive overview of an individual's dental history, including details of dental work, missing teeth, and unique oral characteristics. This information serves as a valuable reference point in linking unidentified remains to missing persons.
Bite mark analysis, another aspect of forensic odontology, involves the examination and comparison of dental impressions left on human skin, objects, or other materials. The distinctiveness of each individual's dentition plays a fundamental role in identifying the perpetrator or excluding individuals from suspicion.
In cases where complete bodies are not available or have undergone extensive decomposition, dental remains are often among the most resilient and reliable sources of information. Teeth can resist extreme conditions, making them useful in identifying victims of natural disasters, mass casualties, or criminal activities.
- Forensic odontologists possess specialized knowledge in dental anatomy, pathology, and dental identification techniques, enabling them to contribute unique insights to the overall forensic investigation process.
- By collaborating closely with other disciplines within forensic medicine, such as forensic anthropology, DNA analysis, and fingerprint identification, forensic odontology reinforces and strengthens the accuracy of victim identification.
- The expertise of forensic odontologists has proven invaluable in mass disaster scenarios, allowing for the swift identification of large numbers of victims, providing closure for families, and aiding in the legal process.
Overall, the field of forensic odontology is a vital component of forensic medicine, providing important contributions to the identification of human remains. Its specialized techniques and reliance on dental evidence ensure that no detail goes unnoticed, furthering the understanding of the circumstances surrounding a person's death and facilitating justice.
Forensic Entomology: Utilizing Insects to Determine Postmortem Interval

Forensic entomology is a field of study within forensic science that investigates the use of insects in determining the estimated time of death in criminal investigations. Insect activity on a decomposing body can provide valuable information, assisting investigators in their quest for the truth.
The Science of Insects
When a human body undergoes decomposition, it becomes an ideal habitat for various insects, such as flies, beetles, and mites. These insects go through distinct life cycles as they feed on the decomposing tissues. By examining the types of insects present, their developmental stages, and the environmental conditions, forensic entomologists can estimate the postmortem interval – the time since death occurred.
Flies, in particular, are often the first insects to arrive at a decomposing body. They lay eggs, typically in body orifices, wounds, or areas of exposed flesh. The eggs hatch into maggots, which voraciously consume the decaying flesh as they mature. By analyzing the maggot size, stage of development, and presence of other insect species, experts can determine the approximate time of oviposition and, subsequently, the time of death.
Beetles are another group of insects frequently encountered in forensic entomology. They are attracted to the drier stages of decomposition, such as when the body moves into the advanced decay or dry remains phase. Beetle larvae, commonly known as dermestid beetles, are often responsible for consuming the dry skin, hair, and ligaments that remain after the maggots have completed their cycle. The presence and developmental stage of beetles can provide additional clues to assist forensic entomologists in estimating the time since death.
Applications in Criminal Investigation
Understanding the life cycles and behaviors of insects that colonize a decomposing body enables forensic entomologists to provide valuable insights in criminal investigations. By collaborating with other forensic professionals, they can help establish a timeline of events, identify any potential discrepancies, and even assist in the determination of the location where the death took place.
In cases where the time of death is disputed or unknown, forensic entomology can provide a scientific basis for analysis. By examining the insect evidence collected from a crime scene, their growth stages and species composition, experts can provide an objective analysis that supports or challenges other forms of evidence. This can ultimately aid in the conviction or exoneration of a suspect.
Additionally, forensic entomology can help uncover cases of foul play, as certain insect species may indicate circumstances such as the presence of drugs or toxins. The study of insect activity on a decomposing body adds another layer of scientific knowledge to the field of forensic medicine, contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of the circumstances surrounding a person's death.
FAQ
What is forensic medicine?
Forensic medicine is a branch of medicine that deals with the application of medical knowledge to legal matters, including the investigation of crimes and identification of victims.
Why do people dream of visiting the morgue?
People may dream of visiting the morgue due to a variety of reasons. Some individuals who are fascinated by forensic medicine and crime investigation may have a desire to witness the process firsthand. Others may have a morbid curiosity or a need for closure in relation to a loved one's death.
What can be learned from visiting a morgue?
A visit to a morgue can provide a fascinating insight into the world of forensic medicine. Visitors can learn about the process of autopsies, the techniques used to determine cause of death, and the role of forensic professionals in criminal investigations. It can also offer a chance to understand the impact of violent crimes on society and the work done to bring justice to victims.



