Dwelling within the realm of slumber, we often find ourselves entranced by vivid visions that convey our deepest fears and desires. These nocturnal reveries, though cryptic in nature, bear witness to the intricacies of our subconscious minds. Among these ethereal episodes, one theme frequently emerges - the potential for the untimely arrival of new life. This nocturnal exploration delves into the multitude of reasons leading to the premature initiation of childbirth, the associated risks, and the profound impact it can have on both mother and child.
Discerning the enigmatic messages hidden within these dreams requires a comprehensive understanding of the factors that may trigger the premature onset of labor. Numerous synonyms are employed in this narrative to encompass the myriad circumstances that provoke this delicate and precarious situation. Exploring the elemental causes that transpire in the realm of fantasy offers valuable insights into the complex web of reality.
Within this labyrinth of the mind, stirring anxieties and uncertainties are reflected through the seamless fabric of slumber. These dreams may be sparked by a hodgepodge of physiological, emotional, or environmental factors, each contributing to the tapestry of fragmented nocturnal visions.
While the origins of these nocturnal premonitions can be multifaceted, it is essential to recognize the substantial risks inherent in premature childbirth, the apex of maternal vulnerability and fetal delicacy. By harnessing the power of synonyms, we shed light on the dangers that loom over this temporal aberration, cautioning us against the precipitous arrival of newborn life. The consequences of early labor can be severe, encompassing not only the physical health of both mother and child but also the long-term emotional and societal repercussions that may follow.
Understanding Premature Labor: Definition and Incidence

Premature labor is a condition that occurs before the expected time of delivery, posing potential risks to both the mother and the baby. This section aims to provide an in-depth understanding of the definition and incidence of premature labor, shedding light on its significance and prevalence.
Definition: Premature labor refers to the onset of labor before the 37th week of pregnancy. It is a critical event that can result in the delivery of a premature baby, compromising their development and health.
Incidence: The incidence of premature labor has been observed to vary among different populations and is influenced by diverse factors. It is an important health concern worldwide, impacting a significant number of pregnancies every year.
By examining the definition of premature labor and its incidence, we can gain a deeper comprehension of the challenges and importance of this condition. This understanding lays the foundation for further exploration into the causes, risks, and impacts associated with premature labor, which will be discussed in subsequent sections.
Factors Contributing to Premature Labor: Exploring the Causes
Understanding the factors that contribute to premature labor is crucial in identifying the potential causes behind this complex and challenging condition. By examining various elements, we can gain insights into the underlying triggers that may lead to early delivery, offering hope for effective prevention and management strategies.
1. Maternal Health:
- Maternal health plays a pivotal role in pregnancy outcomes, and certain conditions may increase the risk of premature labor. Factors such as chronic diseases, infections, pre-existing medical conditions, and lifestyle choices can significantly impact the likelihood of premature birth.
- Inflammation within the maternal body can also exert influence, as elevated levels of inflammatory markers have been associated with an increased risk of premature labor.
2. Uterine Issues:
- The structure and functionality of the uterus are vital in maintaining a healthy pregnancy, and any disturbances can potentially trigger premature labor. Uterine abnormalities, such as an incompetent cervix or uterine fibroids, may influence the occurrence of preterm birth.
- Additionally, certain uterine infections, such as bacterial vaginosis or intrauterine infections, have been linked to an elevated risk of premature labor.
3. Hormonal Imbalances:
- Hormonal imbalances can disrupt the delicate balance required for maintaining a full-term pregnancy. Fluctuations in progesterone levels, responsible for maintaining the uterine lining, can potentially contribute to the onset of premature labor.
- Inadequate production or abnormal regulation of other hormones, such as oxytocin or cortisol, can also influence uterine contractions and cervix dilation, leading to preterm birth.
4. Environmental Factors:
- External influences can impact the risk of premature labor. Factors such as exposure to certain toxins, pollutants, or excessive stress levels during pregnancy have been associated with an increased likelihood of early delivery.
- Living conditions, including suboptimal access to healthcare, socioeconomic disparities, and inadequate prenatal care, can also contribute to the prevalence of premature labor.
By delving into these diverse factors that contribute to premature labor, we can gain significant insights into the intricate web of causes and work towards devising targeted interventions and preventive measures. A comprehensive understanding of these contributing factors is instrumental in reducing the burden associated with preterm birth and ensuring healthier outcomes for both mother and baby.
Maternal Well-being and the Effects of Preterm Birth

When discussing the topic of premature labor, it is essential to consider the impact it has on the mother's overall health and well-being. The effects of preterm birth extend far beyond the immediate birth experience and can have lasting consequences for the mother's physical and emotional well-being.
One of the primary concerns for mothers who experience preterm labor is the potential for complications during and after delivery. These complications can range from postpartum hemorrhage to infections and require immediate medical attention to ensure the mother's safety and recovery. Additionally, preterm labor can lead to increased anxiety and stress levels for the mother, impacting her mental health both during and after the birthing process.
Furthermore, the physical toll of preterm labor on the mother's body cannot be overlooked. The premature onset of labor puts additional strain on the mother's reproductive system and can lead to complications such as cervical incompetence or uterine rupture. These complications can result in long-term health issues for the mother, affecting her ability to conceive and carry future pregnancies.
In addition to the physical repercussions, the psychological impact of preterm labor and the subsequent birth can be profound. Mothers who experience premature birth may face feelings of guilt, sadness, and disappointment due to the inability to carry their baby to full term. These emotions can have long-lasting effects on the mother's mental health, potentially leading to postpartum depression or anxiety.
Supporting the well-being of mothers who have experienced premature labor is crucial in ensuring their overall recovery and adjustment to the challenges they may face. Providing emotional support, counseling, and access to necessary medical resources are all important components of a comprehensive care plan for mothers dealing with the effects of preterm birth.
It is essential for healthcare providers and society as a whole to recognize the impact of preterm labor on maternal health. By addressing the physical and emotional needs of mothers who have experienced premature birth, we can strive to minimize the long-term effects and support their journey towards healing and well-being.
The Impact of Environmental Factors on the Onset of Preterm Birth
In this section, we will explore the significant role that surrounding environmental factors play in the occurrence of preterm birth, a phenomenon associated with the delivery of an infant before completing 37 weeks of gestation. While the causes, risks, and impacts of preterm birth have been extensively studied, understanding the influence of environmental factors is crucial in comprehending the complex nature of this condition. Through identifying and addressing these factors, we can strive to reduce the occurrence of preterm birth and improve the overall health outcomes for both mothers and infants.
Environmental stressors encompass a range of external factors that may contribute to the onset of preterm labor. These stressors can be physical, such as exposure to air pollution, harmful chemicals, or extreme temperatures, or psychosocial, including maternal stress, socioeconomic disparities, or inadequate social support. Each of these stressors has the potential to disrupt the delicate balance of pregnancy, potentially leading to premature birth.
The impact of air pollution on the risk of preterm birth has been widely studied, with research suggesting a correlation between exposure to polluted air and an increased likelihood of preterm labor. Pollutants, such as particulate matter and nitrogen dioxide, can penetrate the respiratory system, causing systemic inflammation and oxidative stress, ultimately compromising the integrity of the pregnancy. Additionally, certain occupations that involve exposure to hazardous substances, such as chemicals or fumes, have also been implicated as potential risk factors for preterm birth.
Psychosocial factors can also significantly impact the onset of premature labor. Maternal stress, particularly chronic stress, has been shown to have detrimental effects on pregnancy outcomes, including an increased risk of preterm birth. Socioeconomic disparities, inadequate social support, and lack of access to healthcare resources further exacerbate the negative impact of stress on pregnancy, highlighting the importance of addressing and reducing these factors for improved maternal and fetal health.
Conclusion
Considering the immense impact of environmental factors on the occurrence of preterm birth, it is evident that a holistic approach is necessary to effectively prevent and manage this condition. Identifying and mitigating physical and psychosocial stressors, promoting clean and healthy environments, and ensuring adequate support and resources for expectant mothers are key steps towards reducing the incidence of preterm birth and improving the overall well-being of both mothers and infants.
Risk Factors for Preterm Birth: A Deeper Examination

Delving into the intricacies of preterm birth, it is vital to explore the various factors that may contribute to this significant health concern. By understanding the array of elements that increase the likelihood of early delivery, we can gain valuable insights into the prevention and management of premature labor. In this section, we will closely examine the potential risk factors associated with preterm birth, exploring their impact on both the expectant mother and her unborn baby.
Maternal Factors:
One essential aspect to consider when evaluating the risk factors for preterm labor is the mother's health and well-being. Certain maternal conditions, such as hypertension, diabetes, or infections during pregnancy, have been identified as potential contributors to preterm birth. Additionally, maternal age, socioeconomic status, and lifestyle choices, including smoking and substance abuse, can all play a role in increasing the chances of premature labor.
Previous Obstetric History:
The occurrence of preterm birth is often influenced by past pregnancies and obstetric history. Women who have previously experienced preterm delivery are at increased risk of recurrence. Other factors, such as multiple pregnancies (twins, triplets, etc.), a history of miscarriage, or complications such as placental abruption or cervical insufficiency, may also elevate the likelihood of premature labor.
Poor Prenatal Care:
The level and quality of prenatal care received throughout pregnancy can significantly impact the risk of preterm birth. Adequate prenatal care involves regular check-ups, proper nutrition, and monitoring of any complications or risk factors. Lack of access to adequate healthcare, insufficient prenatal visits, or inadequate knowledge about proper prenatal care can all contribute to an increased risk of premature labor.
Psychosocial Factors:
It is essential to recognize the influence of psychosocial factors on the occurrence of preterm birth. High levels of stress, anxiety, depression, or significant life events can potentially trigger premature labor. Social determinants of health, such as poor social support, low socioeconomic status, and limited access to education or resources, can also contribute to an increased risk of preterm birth.
Understanding the complex web of risk factors associated with preterm birth is crucial in our efforts to minimize its occurrence. By identifying and addressing these factors both on an individual and societal level, we can work towards ensuring healthier outcomes for expectant mothers and their babies.
Recognizing Symptoms of Premature Birth: Indicators to Remain Alert For
Identifying the warning signs of a premature birth can be crucial in ensuring the well-being of both the mother and the baby. Familiarizing oneself with the possible indications allows for early detection and prompt medical attention, potentially reducing the risks associated with premature labor.
1. Contractions: One of the primary indicators of premature labor is experiencing regular contractions before the 37th week of pregnancy, often accompanied by a frequent tightening sensation in the lower abdomen or back, resembling menstrual cramps. These contractions may persist even after resting or changing positions.
2. Vaginal bleeding: The presence of any amount of vaginal bleeding, ranging from light spotting to heavier bleeding, should never be considered normal during pregnancy, particularly before the due date. Vaginal bleeding can signify the onset of premature labor and should be promptly addressed by a healthcare professional.
3. Pelvic pressure: An increased, persistent sensation of pressure in the pelvic area can be an indication of the cervix starting to efface or dilate prematurely. This sensation may feel similar to the baby's head pushing against the pelvis and may be accompanied by a frequent urge to urinate.
4. Fluid leakage: The presence of a watery vaginal discharge that can potentially soak through underwear may be a sign of the amniotic sac rupturing prematurely. This rupture of the membranes can lead to an increased risk of infection and necessitates immediate medical attention.
5. Backache: Persistent lower back pain or discomfort, which may radiate to the abdomen, can sometimes indicate the onset of premature labor. This backache might feel different from typical pregnancy-related back pain and may not subside with rest or additional support.
It is vital to remember that these symptoms, even when present, do not definitively indicate premature labor. However, if any of these signs are experienced, seeking immediate medical advice is crucial for accurate assessment and appropriate management.
Diagnosing Premature Labor: Medical Tests and Procedures
In the pursuit of determining the onset of labor before the expected timeframe, healthcare providers employ a range of medical tests and procedures. These diagnostic tools are used to assess the likelihood of premature labor and evaluate its potential risks and implications. By utilizing an array of methods, medical professionals can effectively diagnose and monitor the condition, allowing for timely intervention and appropriate management.
| Medical Test/Procedure | Description |
|---|---|
| Cervical Length Measurement | This non-invasive procedure involves the measurement of the length of the cervix using ultrasound technology. A shortened cervix is often associated with an increased risk of premature labor. By monitoring changes in cervical length over time, healthcare providers can assess the likelihood of preterm birth. |
| Fetal Fibronectin Test | The fetal fibronectin test is performed by collecting a sample of vaginal fluid to determine the presence of fetal fibronectin, a protein that serves as a marker for possible preterm labor. This test is particularly useful in ruling out premature labor when a woman experiences symptoms such as contractions prior to term. |
| Amniocentesis | Amniocentesis involves the extraction of a small amount of amniotic fluid from the sac surrounding the fetus. This procedure is typically conducted between weeks 15 and 20 of pregnancy to assess the risk of preterm labor. The collected fluid is analyzed for various markers and indicators that can inform healthcare providers about the condition of the baby and the likelihood of premature birth. |
| Ultrasound Examination | Ultrasound examinations are a common diagnostic tool used to monitor the health of the fetus and assess signs of preterm labor. By utilizing sound waves, healthcare providers can visualize the uterus, cervix, and the baby, allowing for the identification of any abnormalities or markers associated with premature labor. |
| Hormone Level Testing | Testing hormone levels, such as progesterone, can aid in the diagnosis of premature labor. Hormonal imbalances or deficiencies can contribute to an increased risk of preterm birth. By assessing hormone levels, healthcare providers can determine appropriate interventions or treatments to prevent premature labor or manage its consequences. |
Through the utilization of these medical tests and procedures, healthcare providers can effectively diagnose, monitor, and manage the risks associated with premature labor. Early detection and intervention are crucial in ensuring the best possible outcomes for both the mother and the baby.
Strategies for Minimizing the Risk of Preterm Birth
Discovering ways to mitigate the likelihood of delivering a baby ahead of schedule is of utmost importance for expectant parents. By implementing various strategies, one can potentially reduce the chances of premature birth and its associated complications.
Creating a strong foundation for a healthy pregnancy involves a combination of lifestyle changes, regular prenatal care, and awareness of potential risk factors. This section aims to delve into a range of techniques and precautionary measures that can help expecting mothers maintain a full-term pregnancy.
First, it is crucial to focus on maintaining a well-balanced and nutritious diet. Providing the body with essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can promote healthy fetal growth and development, potentially reducing the risk of preterm labor.
In addition to proper nutrition, engaging in regular physical activity, such as moderate-intensity exercises approved by healthcare professionals, can contribute to a healthy pregnancy. Staying physically active helps manage weight gain, enhances overall strength, and aids in stress reduction, all of which play a role in minimizing the likelihood of premature labor.
Furthermore, understanding and addressing potential risk factors is key in preventing preterm birth. Women with a history of preterm delivery, certain medical conditions, or complications during pregnancy should consult their healthcare provider to develop an individualized plan. Proactive management of such factors can significantly reduce the risk and potential impact of premature labor on both the mother and the baby.
Lastly, receiving comprehensive prenatal care is paramount. Scheduling regular check-ups and following recommended prenatal visit schedules allows healthcare professionals to monitor the progress of pregnancy closely. Any signs of early labor or potential risk factors can be addressed promptly, potentially preventing premature birth and its associated complications.
By embracing these preventative strategies, expectant parents can increase their chances of delivering a healthy baby at full term. The following sections will delve deeper into specific causes, risks, and impacts of premature labor to better inform and educate expectant parents about their journey towards a safe and successful pregnancy.
The Long-Term Consequences of preterm birth on Childhood Development
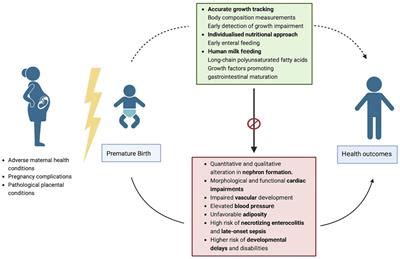
One of the major concerns surrounding premature birth is the potential long-term consequences it may have on the child's development. Early delivery can pose a range of challenges that can impact various aspects of a child's life, from physical health to cognitive abilities. Understanding these potential effects is crucial for parents, healthcare professionals, and educators to provide the necessary support and interventions to mitigate any adverse outcomes.
Physical health: Children who are born prematurely often face an increased risk of experiencing a variety of physical health issues throughout their lives. These may include respiratory problems, cardiovascular complications, and a higher susceptibility to infections. Additionally, preterm infants may be more likely to develop chronic conditions such as asthma and obesity, requiring long-term management and healthcare support.
Cognitive development: The impact of prematurity on cognitive development can vary widely depending on the gestational age at birth and other individual factors. While some children may experience no long-term effects, others may face challenges in areas such as attention, memory, problem-solving, and academic performance. Moreover, preterm birth has been associated with a higher risk of neurodevelopmental disorders, including autism spectrum disorder and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Social-emotional well-being: Premature birth can also have implications for a child's social-emotional well-being. Preterm infants may face difficulties in forming secure attachments and establishing social relationships. They may exhibit higher levels of anxiety, impulsivity, and emotional instability, impacting their overall quality of life and ability to navigate social interactions effectively.
Educational outcomes: The effects of premature birth on educational outcomes are significant. Children born prematurely often require additional support and accommodations to thrive academically. They may experience delays in language development, reading comprehension, and mathematical abilities. Early intervention programs and individualized educational plans can play a crucial role in optimizing educational outcomes for these children.
In conclusion, premature birth can have long-term effects on a child's physical health, cognitive development, social-emotional well-being, and educational outcomes. Recognizing and addressing these challenges early on can help provide the necessary support and interventions to promote the child's overall well-being and success.
FAQ
What are the causes of premature labor?
Premature labor can be caused by several factors, including infections, high blood pressure, multiple pregnancies, smoking, drug abuse, and certain medical conditions of the mother.
What are the risks associated with premature labor?
Premature labor carries various risks for both the baby and the mother. The baby may experience respiratory problems, developmental issues, and long-term disabilities. The mother may face increased chances of infection, hemorrhage, and emotional distress.
What are the impacts of premature labor on the baby?
Premature labor can have significant impacts on the baby's health and development. The baby may have difficulty breathing, feeding, and regulating body temperature. They may also be at higher risk of infections, cognitive impairments, and developmental delays.



