Within the intricate realm of human health, there exists an enigmatic condition that haunts our subconscious, lurking within the depths of our dreams–an unfathomable disturbance that fills our minds with trepidation and unease. A mysterious ailment known as cerebral hemorrhage, this elusive affliction silently disrupts the delicate equilibrium of our most vital organ, the brain. As we embark on a quest to comprehend the intricacies of this intriguing phenomenon, we shall navigate through the intricate tapestry of its causes, its telltale signs, and the diverse therapeutic strategies currently employed in an attempt to tame this relentless adversary.
Indubitably, the origins of cerebral hemorrhage arise from a plethora of contributory factors, which intertwine like the delicate threads of a spider's web. Etiologically speaking, the primary instigator behind this life-altering condition lies within the disequilibrium of the delicate arterial network feeding the brain. Disruption to the cerebral blood vessels, whether through hypertension, trauma, or abnormal structural formations, can lead to a catastrophic rupture, instigating an unwarranted release of blood within the cranial cavity. This rupture, akin to a crack in a dam, sets forth a cascading chain of events, undermining the intricate neural functions of this precious organ.
As this enigmatic event unfolds, numerous signs and symptoms emerge, serving as harbingers of the impending storm. Ranging from subtle warnings to blatant manifestations, the consequences of cerebral hemorrhage can materialize in various ways, reflecting the heterogeneity of this calamity. The beleaguered victim may experience an excruciating headache, akin to a relentless thunderstorm ravaging the delicate landscape of their consciousness. Profound weakness and numbness can seize their limbs, a ghostly paralysis that steals away their mobility and autonomy. At times, their speech may falter, their words lost in a labyrinth of tangled neural pathways. By recognizing the diverse tapestry of manifestations, we may yet unlock the secrets hidden within this perplexing condition.
Amidst the chaos and the uncertainty, hope glimmers on the horizon in the form of various treatment modalities. Within the arsenal of therapeutic interventions, a multifaceted approach seeks to alleviate the devastating repercussions that cerebral hemorrhage imposes on the lives of its victims. Accessing the affected blood vessels through minimally invasive procedures, skilled physicians defy the intrusion of surgical instruments to repair the damage and restore the flow of life-sustaining blood. In other cases, pharmacological interventions aim to tame the underlying hypertension that often precipitates this disastrous event. Through the combined efforts of medical professionals and the resilience of the human spirit, a glimmer of optimism illuminates the path toward recovery.
Understanding Brain Hemorrhage: Essential Information to Know

Introduction: In this section, we will delve into the intricate details surrounding brain hemorrhage, a condition that can have severe consequences on an individual's health. By exploring the underlying causes, recognizable symptoms, and available treatments, we aim to equip you with a comprehensive understanding of this medical condition. Throughout this discussion, we will shed light on the delicate nature of the brain and the potential dangers associated with hemorrhages, emphasizing the importance of recognizing the signs and seeking timely medical intervention.
The Intricacies of Brain Bleeding: With a focus on brain hemorrhage, also referred to as intracranial bleeding, we aim to explore the complexity and severity of the condition. By providing detailed insights into the intricacies of its development, we will highlight the significance of understanding the various factors that can contribute to this medical emergency, including trauma, high blood pressure, aneurysms, or underlying health conditions.
Recognizing the Telltale Signs: Understanding the symptoms associated with brain hemorrhage plays a vital role in early detection and prompt intervention. By familiarizing yourself with the warning signs, such as severe headaches, sudden vision changes, loss of consciousness, or difficulty speaking, you can potentially save lives by ensuring immediate medical attention is sought. We will explore these telltale signs in depth, shedding light on their significance and the urgency they demand.
Effective Treatment Approaches: When it comes to managing brain hemorrhage, early diagnosis and appropriate treatment options are crucial for optimal outcomes. In this section, we will discuss the available treatment approaches, including surgical interventions, medication, and therapies aimed at reducing bleeding, preventing complications, and promoting recovery. By understanding the different treatment modalities, you can gain insight into the comprehensive care and support necessary for individuals affected by brain hemorrhages.
Conclusion: In conclusion, familiarizing oneself with the complexities of brain hemorrhage, recognizing its symptoms, and understanding the available treatment approaches is of utmost importance in dealing with this serious medical condition. By raising awareness and providing comprehensive knowledge, we empower individuals to take proactive measures in seeking timely medical attention and supporting ongoing recovery. Remember, knowledge is a powerful tool in safeguarding your well-being and the well-being of those around you.
The Factors Behind Brain Bleeding: A Deep Dive into the Causes
Brain bleeding, in a realm where the delicate balance of blood vessels within the intricate network of the mind is disrupted, is a grave concern. Understanding the factors that contribute to this potentially life-threatening condition is crucial for both medical professionals and the general public. By exploring these factors, we can gain insights into the root causes and pave the way for preventative measures and more effective treatments.
One major factor that can lead to brain bleeding is hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure. When the force exerted on the blood vessel walls exceeds the recommended range, the vessels can weaken and become prone to rupture. This rupture can result in intracranial bleeding, leading to various neurological complications.
Another significant cause of brain bleeding is aneurysms, which are abnormal bulges in the blood vessels. These weakened spots can grow over time and reach a critical point where they rupture, causing blood to spill into the brain. Aneurysms can result from several factors, including genetic predisposition, certain medical conditions, or lifestyle choices.
Additionally, trauma, such as head injuries or accidents, can also trigger brain bleeding. Sudden impact or a forceful blow to the head can disrupt the integrity of blood vessels, causing them to tear and bleed. This type of brain bleeding, known as traumatic brain injury-related hemorrhage, requires immediate medical attention to mitigate potential long-term damage.
Furthermore, underlying medical conditions, such as arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) and cerebral amyloid angiopathy, can contribute to brain bleeding. AVMs are abnormal tangles of blood vessels that can disrupt the normal circulation of blood, leading to increased pressure and potential ruptures. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy, on the other hand, involves the accumulation of amyloid protein in the walls of blood vessels, making them more fragile and prone to bleeding.
| Factors contributing to Brain Bleeding |
|---|
| Hypertension |
| Aneurysms |
| Trauma |
| Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs) |
| Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy |
In conclusion, brain bleeding can have various causes, each playing a significant role in the development of this serious medical condition. Identifying and understanding these factors is crucial in order to effectively prevent, diagnose, and treat brain bleeding. By addressing the underlying causes, medical professionals can strive towards improved outcomes and better overall care for those affected by this condition.
Recognizing the Signs of Hemorrhage in the Brain: Key Indicators
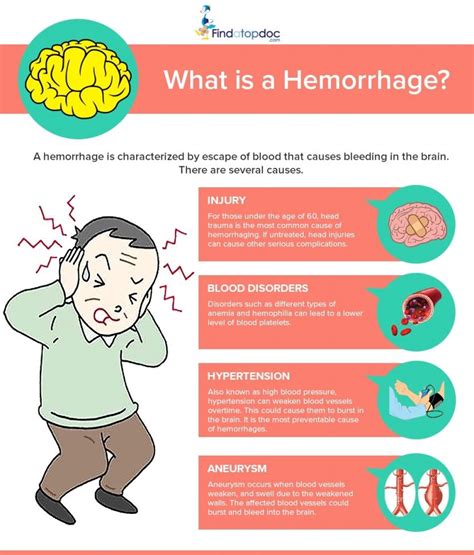
Identifying the manifestation of brain bleeding is critical for early detection and prompt medical intervention. By recognizing the various symptoms associated with this condition, individuals can take appropriate action to seek immediate medical attention, potentially saving lives and preventing further complications.
1. Headache
- Persistent and severe head pain
- Throbbing sensation
- Pain that worsens with movement or exertion
2. Neurological Dysfunction
- Sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the body
- Difficulty speaking or slurred speech
- Loss of coordination and balance
- Vision problems, such as blurred or double vision
- Confusion and disorientation
3. Altered Mental State
- Unexplained bouts of dizziness or lightheadedness
- Memory loss or amnesia
- Unusual irritability or mood swings
- Difficulty concentrating or staying focused
4. Nausea and Vomiting
- Feeling nauseous or experiencing stomach discomfort
- Recurrent episodes of vomiting
5. Seizures
- Unprovoked seizures, particularly in individuals with no history of seizures
- Convulsions or involuntary muscle contractions
While these symptoms may not always indicate brain bleeding, they serve as crucial warning signs that should not be ignored. If you or someone you know experiences any of these indicators, it is imperative to seek medical attention immediately for a thorough evaluation and appropriate treatment.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Brain Bleeding: Urgency Matters
In the context of brain bleeding, it is crucial to understand the importance of seeking medical attention promptly when faced with potential symptoms. Recognizing the urgency of the situation can make a significant difference in the outcome and potential complications. Proper understanding of when to seek medical attention can help minimize the risks associated with brain bleeding and ensure timely and appropriate treatment is received.
Timely Identification of Symptoms:
If you experience symptoms such as severe headache, sudden loss of consciousness, seizures, slurred speech, confusion, weakness or numbness in the extremities, or visual disturbances, it is important to recognize these signs as potential indications of brain bleeding. Ignoring or downplaying these symptoms can lead to worsening of the condition and potentially life-threatening consequences. Immediate medical attention is strongly advised if any of these symptoms occur.
High-Risk Scenarios:
While brain bleeding can occur spontaneously, there are certain situations where the risk is significantly heightened. Being aware of these scenarios is crucial in understanding when to seek medical attention urgently. Examples include significant head trauma, particularly if accompanied by loss of consciousness, repeated vomiting, or behavior changes. Additionally, individuals with preexisting conditions such as high blood pressure, blood clotting disorders, or a history of aneurysms are at a higher risk and should be vigilant in monitoring any potential symptoms. If you find yourself in any of these high-risk scenarios and experience symptoms related to brain bleeding, immediate medical attention is necessary.
Err on the Side of Caution:
In cases where there is uncertainty about the severity of symptoms or the likelihood of brain bleeding, it is always better to err on the side of caution and seek medical attention. Prompt evaluation by a healthcare professional can provide reassurance, early intervention, and potentially life-saving treatment if necessary. It is important to remember that brain bleeding is a serious medical condition that requires immediate attention, and waiting to seek medical help may lead to irreversible damage. When in doubt, it is crucial to prioritize your health and seek urgent medical attention.
Conclusion:
Recognizing the importance of seeking medical attention promptly when faced with potential brain bleeding symptoms is paramount. The urgency with which one seeks medical help can make a significant difference in the outcome. Knowing how to identify symptoms, understanding high-risk scenarios, and erring on the side of caution are crucial steps in ensuring timely intervention and appropriate treatment. Your health should never be compromised when it comes to brain bleeding. Remember, seeking medical attention without delay can potentially save lives and minimize the long-term impact of brain bleeding.
Treatment Options for Cerebral Hemorrhage: From Medications to Surgical Intervention
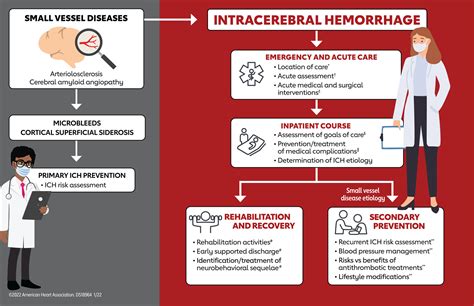
When it comes to addressing cerebral hemorrhage, there are a range of treatment options available that can effectively manage this serious medical condition. From medications to surgical intervention, healthcare professionals employ various approaches to prevent further damage, relieve symptoms, and promote recovery.
Medications play a crucial role in the treatment of cerebral hemorrhage. Doctors often prescribe drugs that help reduce blood pressure, control seizures, and prevent complications such as swelling in the brain. These medications not only manage symptoms but also promote the healing process, allowing the affected individual to regain their health.
In some cases, surgical intervention is necessary to treat cerebral hemorrhage. One common procedure is called a craniotomy, where a section of the skull is temporarily removed to access the bleeding area within the brain. This allows surgeons to accurately locate and remove the blood clot or repair the damaged blood vessels, effectively stopping the bleeding and reducing the risk of further brain injury.
Another surgical option is an endovascular procedure, such as coiling or embolization, which involves inserting tiny coils or a glue-like substance into the affected blood vessel to stop the bleeding. These minimally invasive techniques offer a shorter recovery time compared to traditional open surgery and can be a viable option for certain cases of cerebral hemorrhage.
In addition to medications and surgical interventions, rehabilitation plays a crucial role in the overall treatment of cerebral hemorrhage. Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy help individuals regain and improve their motor skills, cognitive abilities, and communication skills. This holistic approach aims to restore functionality and maximize the individual's quality of life after the hemorrhage.
It is important to note that the choice of treatment option depends on various factors, including the severity of the cerebral hemorrhage, the individual's overall health, and the specific location of the bleeding. Therefore, it is vital for healthcare professionals to carefully assess each case and customize the treatment plan accordingly.
Preventing Brain Hemorrhage: Lifestyle Modifications and Reducing Risk Factors
Avoiding brain bleeding is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. By adopting certain lifestyle changes and reducing risk factors, you can significantly lower the chances of experiencing a brain hemorrhage. This section focuses on providing practical measures and information to help prevent this condition from occurring.
1. Healthy Diet: Adopting a balanced and nutritious diet is essential for overall health and reducing the risk of brain bleeding. Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your meals. Limit the consumption of processed foods, saturated fats, and excess salt, as they can contribute to various health issues, including high blood pressure. |
2. Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity is beneficial for both your body and mind. It helps maintain a healthy weight, promotes good blood circulation, and reduces the risk of hypertension and other cardiovascular diseases. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous aerobic exercise per week, along with strength training activities. |
3. Managing Hypertension: High blood pressure is a major risk factor for brain hemorrhage. Regularly monitor your blood pressure and take necessary steps to keep it within a healthy range. This may include reducing salt intake, limiting alcohol consumption, quitting smoking, and regularly taking prescribed medications if recommended by your healthcare provider. |
4. Avoiding Excessive Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to high blood pressure and other health issues. Limit your alcohol intake to moderate levels or avoid it altogether to reduce the risk of brain bleeding and maintain overall health. |
5. Preventing Head Injuries: Taking precautions to prevent head injuries is crucial in reducing the risk of brain hemorrhage. Always wear helmets and appropriate safety gear during activities that involve a risk of head injury, such as cycling, skateboarding, or certain sports. Additionally, ensure a safe environment in your home to minimize the chances of accidental falls or traumatic incidents. |
By incorporating these lifestyle modifications and risk reduction strategies into your daily life, you can significantly lower the risk of experiencing a brain hemorrhage. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance based on your individual health status and risk factors.
Recovery and Rehabilitation after Hemorrhage in the Brain: The Path to Healing
The process of recovering and rehabilitating after experiencing a hemorrhage in the brain is a critical and multifaceted journey towards healing. This section delves into the various aspects involved in the recovery process, highlighting the importance of patience, perseverance, and comprehensive treatment.
1. Embracing Rest and Gradual Progression:
- Allowing ample rest and giving the brain time to heal is essential during the initial stages of recovery.
- Gradual progression through physical and cognitive activities can help regain strength and functionality over time, but it is crucial to avoid pushing oneself too hard.
- Support from healthcare professionals and loved ones can provide the necessary guidance and encouragement during this period.
2. Rehabilitation Therapies:
- Physical therapy aims to restore motor function, balance, and coordination through targeted exercises and techniques.
- Occupational therapy focuses on rebuilding skills needed for daily activities and improving cognitive abilities.
- Speech and language therapy helps individuals regain speech and language skills affected by the brain bleeding.
3. Emotional and Psychological Support:
- Coping with the aftermath of brain bleeding involves addressing emotional and psychological challenges.
- Individual and group therapy sessions can provide a safe space to express feelings, deal with stress, and develop effective coping mechanisms.
- Support from mental health professionals, family, and friends plays a vital role in ensuring emotional well-being throughout the recovery journey.
4. Medication and Medical Management:
- In some cases, medication may be prescribed to manage symptoms, prevent secondary complications, or aid in the recovery process.
- Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are necessary to monitor progress, address any concerns, and adjust treatment plans if needed.
5. Lifestyle Modifications:
- Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep, can support overall healing and enhance recovery outcomes.
- Avoiding substances such as alcohol and tobacco is crucial, as they can impede the healing process and increase the risk of further complications.
6. Building a Strong Support System:
- Having a network of support consisting of healthcare professionals, family, friends, and support groups can provide valuable encouragement, understanding, and assistance throughout the recovery journey.
- Open communication and seeking help when needed can contribute to a smoother healing process and an improved quality of life after brain bleeding.
In summary, the road to healing after brain bleeding requires a comprehensive approach that includes rest, professional therapies, emotional support, medical management, lifestyle modifications, and a strong support system. By embracing these elements and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals can optimize their chances of recovering and regaining as much functionality as possible.
FAQ
What is brain bleeding?
Brain bleeding refers to a medical condition where there is bleeding in the brain due to the rupture of blood vessels. It can result in various serious symptoms.
What are the causes of brain bleeding?
There are several causes of brain bleeding, including high blood pressure, traumatic brain injury, aneurysm rupture, arteriovenous malformation, and certain medications such as anticoagulants. It is important to identify the underlying cause for appropriate treatment.
What are the symptoms of brain bleeding?
The symptoms of brain bleeding can vary depending on the location and extent of the bleeding. Common symptoms include severe headache, sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the body, difficulty speaking, loss of balance, vomiting, seizures, and altered consciousness. It is crucial to seek immediate medical attention if these symptoms occur.
How is brain bleeding diagnosed?
Diagnosing brain bleeding typically involves a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examination, imaging tests such as CT scan or MRI, and sometimes a lumbar puncture to analyze the cerebrospinal fluid. These diagnostic tools can help determine the presence, location, and severity of brain bleeding.
What are the treatment options for brain bleeding?
The treatment options for brain bleeding depend on the cause, extent, and location of the bleeding. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to stop the bleeding and remove any clots or hematomas. Medications to manage symptoms and control blood pressure may also be prescribed. Rehabilitation and supportive care are often required for recovery.



